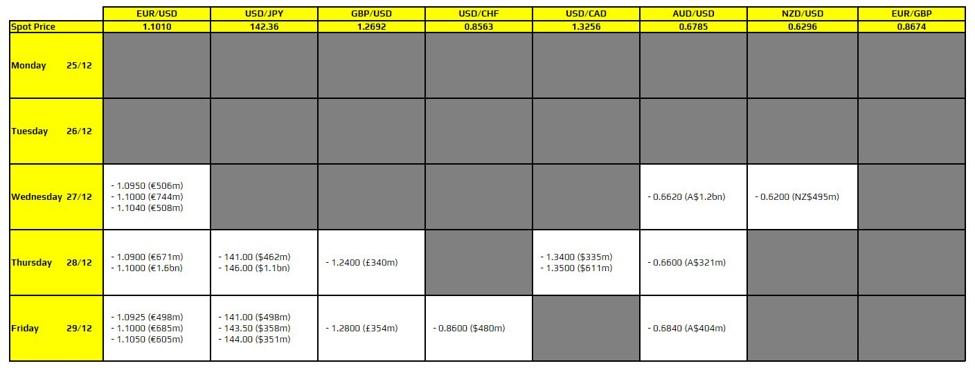
Something unusual is happening at Dollar Tree: The discount retailer said this week that of the 3 million new households that shopped its stores in the third quarter, approximately 60% of those new customers came from households earning more than $100,000 a year.
The trend underscores a deepening split in the American economy. While cumulative inflation has pushed prices up roughly 25% since 2020, wage growth has not kept pace for most households, leaving consumers across the income spectrum hunting for deals.
“Higher income households are trading into Dollar Tree, lower-income households are depending on us more than ever,” Dollar Tree CEO Michael Creedon Jr. told analysts on Wednesday. The Virginia-based chain, where 85% of sales during the quarter were priced at $2 or less, reported same-store sales growth of 4.2%.
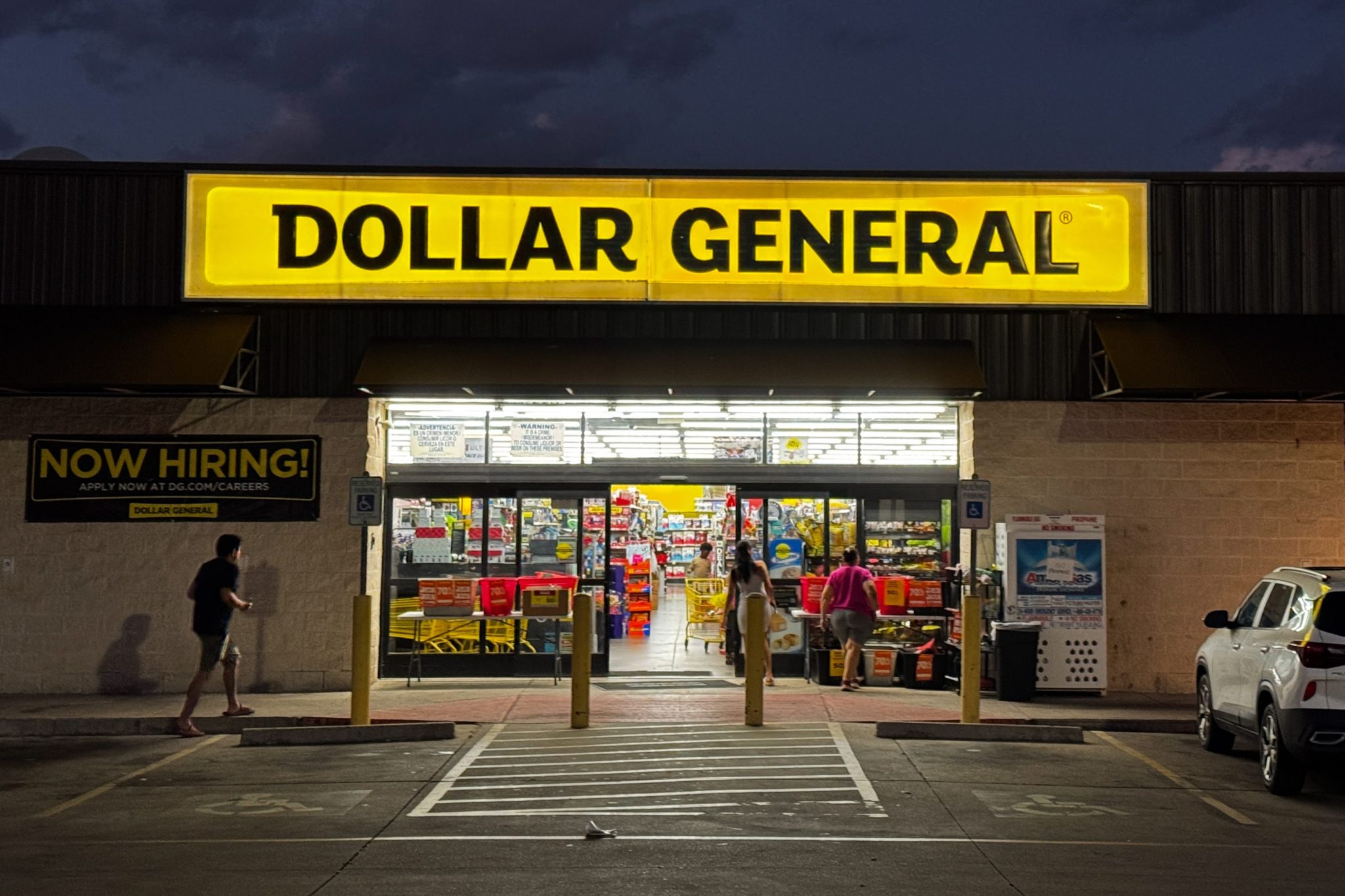
Dollar General, the nation’s largest dollar-store chain with nearly 21,000 locations, reported similar dynamics in its own earnings report this week. CEO Todd Vasos noted “disproportionate growth coming from higher-income households” in the third quarter, as same-store sales rose 2.5% on a 2.5% increase in customer traffic. The company’s net profit climbed 44% to $282.7 million. Discount retail chain Five Below also raised its profit outlook for the rest of the year, lifted by demand for budget-friendly goods and a weaker labor market.
The shift reflects what analysts describe as a “K-shaped” economy, where wealthy Americans—buoyed by stock market gains and appreciating assets—continue spending freely while everyone else tightens their belts. According to an RBC Economics analysis, the top 10% to 20% of income earners are driving consumption growth, while the bottom 80% have minimal financial reserves and are increasingly stretched thin.
Kroger, the nation’s largest supermarket chain, painted a similar picture in its earnings report Thursday. CEO Ron Sargent told analysts the company is “seeing a split across income groups,” with spending from higher-income households remaining “strong” while “middle-income customers are feeling increased pressure, similar to what we’ve seen from lower-income households over the past several quarters.”
Those consumers, Sargent added, are “making smaller, more frequent trips to manage budgets and they are cutting back on discretionary purchases.”
The financial strain is showing up in credit data. U.S. household debt hit a record $18.59 trillion in the third quarter of 2025, with credit card delinquencies climbing to levels not seen since 2011. Meanwhile, the annual inflation rate stood at 3% in September, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
For dollar stores, the influx of wealthier shoppers presents both opportunity and challenge. At Dollar Tree, traffic actually fell 0.3%—the first decline since fiscal 2022—even as the chain gained new customers, because higher-income households visit less frequently than the chain’s core consumers.
Dollar Tree has also been forced to raise prices due to tariffs, a process Creedon acknowledged was a “necessary evil.” The company’s chief financial officer called it “tariff-related stickering activities.”
For this story, Fortune journalists used generative AI as a research tool. An editor verified the accuracy of the information before publishing.