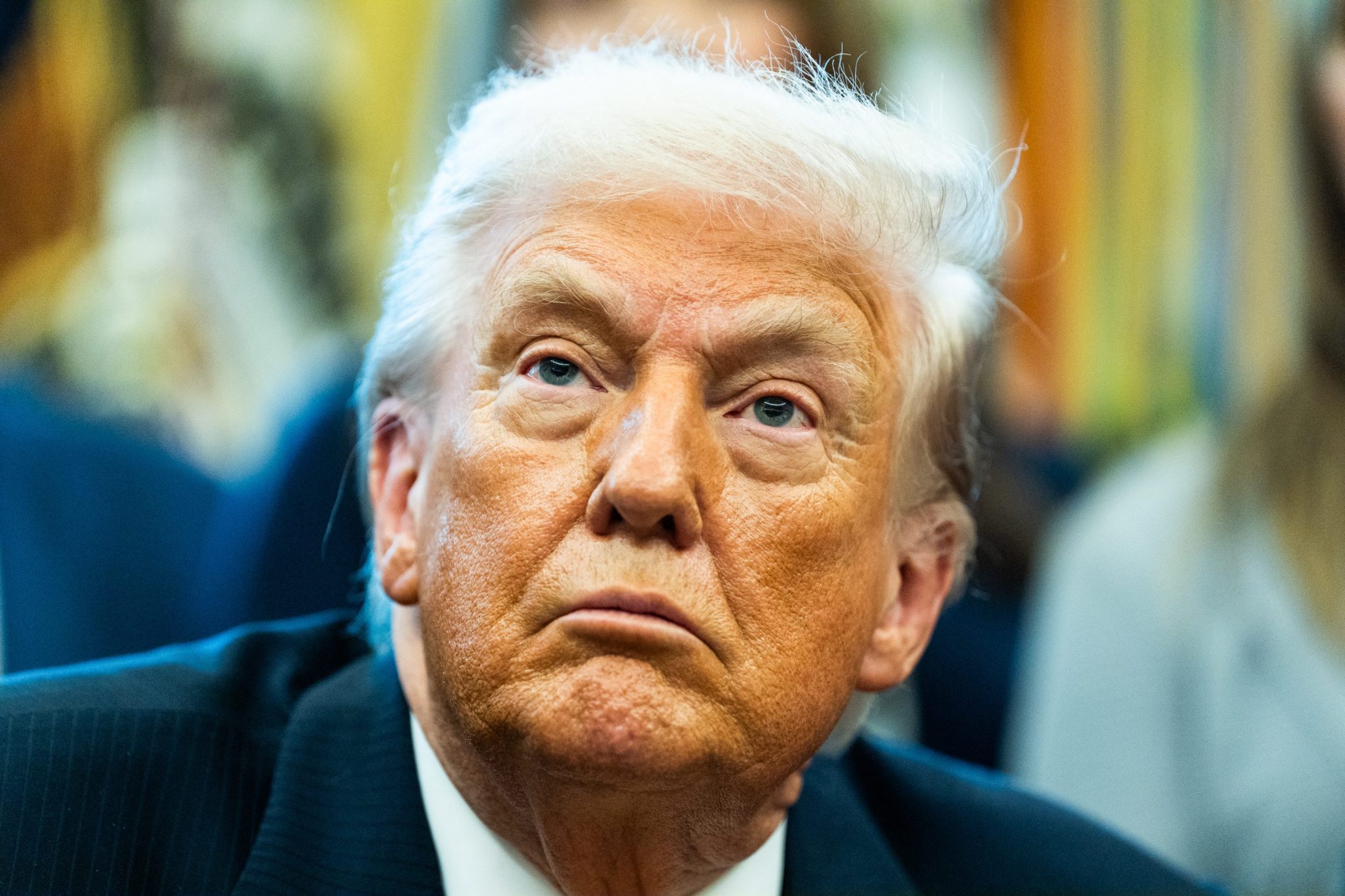
President Trump may be overplaying his hand in negotiations for Greenland, economists are warning, after the Oval Office threatened new tariffs on E.U. countries if they did not support America’s demand to purchase the territory.
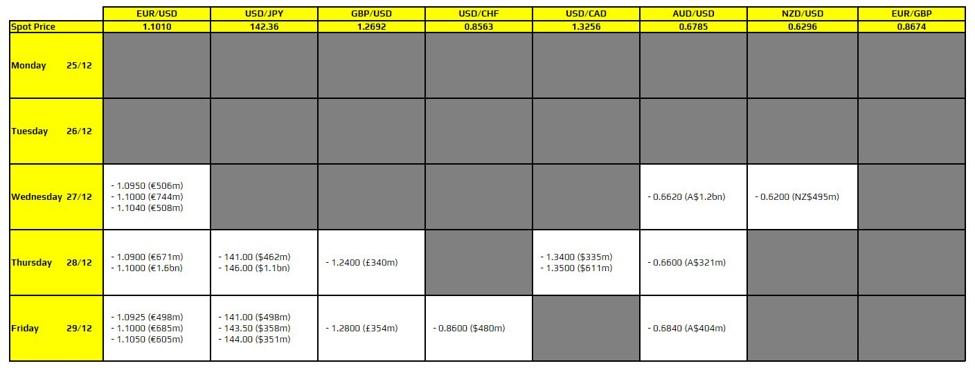
Over the weekend, President Trump posted on Truth Social (a site he owns) that “starting on February 1st, 2026, … Denmark, Norway, Sweden, France, Germany, The United Kingdom, The Netherlands, and Finland, will be charged a 10% tariff on any and all goods sent to the United States of America.
“On June 1st, 2026, the tariff will be increased to 25%. This tariff will be due and payable until such time as a deal is reached for the complete and total purchase of Greenland.”
President Trump believes the U.S. needs to buy the territory (which is not for sale) for national security reasons, claiming China and Russia also want to control the region. He argues that Denmark, of which Greenland is a self-governing, autonomous part of the kingdom, does not have the ability to defend the land.
Trump’s request to purchase land under the jurisdiction of another nation has not gone down well with the Western world. While the U.S. may be the biggest economy on the planet, patience is wearing thin among its allies, after a year of barbed back-and-forths over tariffs and military spending.
This weekend’s power flex may be a stretch too far, economists are now warning, and Trump’s weakness may prove to be America’s voracious spending habits.
Deutsche Bank’s Jim Reid highlighted that Liberation Day tariffs in April were stepped back a week later, after U.S. Treasury yields saw a “scary” session as investors retreated to safety, away from American borrowing.
“Financial markets may play a big part in how this situation resolves itself,” Reid wrote in a note to clients this morning. “The main Achilles Heel of the U.S. is the huge twin deficits. So while in many ways it feels like the U.S. holds the economic cards, it doesn’t hold all the funding cards in a world that will be very disturbed by the weekend’s events.”
Investors, analysts, and world leaders have long wondered when—or if—a debt crisis would occur in one of the nations burdened by a massive deficit. While the likes of Japan, the U.K., and France are by no means balancing their books, America’s $38 trillion deficit dwarfs its counterparts. While a great deal of that debt is held by the public (including the Fed, where President Trump is also in hot water), vast sums are also owned by foreign governments and overseas investors.
This exposure—to the tune of $8 trillion—ING pointed out, may be something European leaders decide to remind the White House of. Europe being America’s largest lender “illustrates the deep interdependence between the U.S. and Europe but also shows that, at least theoretically, Europe also has leverage on the U.S.,” wrote Carsten Brzeski, global head of macro, and Bert Colijn, chief economist for the Netherlands. The duo added: “Whether in practice, Europe would really engage in a ‘Sell America Inc’ season is a completely different question. There is very little the EU could do to force European private sector investors to sell USD assets; it could only try to incentivise investments in EUR assets.”
Alternative measures: An ACI
The EU also has a weapon in its arsenal that it has yet to deploy. French President Emmanuel Macron has suggested now is the time to use the E.U.’s Anti-Coercion Instrument (ACI). The tool is a set of countermeasures against any foreign powers that unduly interfere in the policy choices of the E.U. or its member states, by restricting U.S. companies from accessing the European market, banning them from bidding for government work, restricting trade, and curtailing foreign investment.
The E.U. could also impose new tariffs on about $100 billion of its imports from the U.S.
This, Goldman Sachs believes, is likely to be one of the reactions European leaders are now weighing. Analysts Sven Jari Stehn and Giovanni Pierdomenico wrote this weekend that the legislation had been designed precisely for situations like this—though perhaps not with a strong ally like the U.S. in mind.
The duo wrote: “Starting the activation does not mean implementation (which requires several steps) but signals potential E.U. action and allows time for negotiation. The ACI could involve a range of policy tools broader than tariffs, such as investment restrictions, taxation of U.S. assets and services.” On services, the E.U. conveniently holds a surplus over the U.S., meaning it would inflict greater harm in this particular industry compared to similar action from across the Atlantic.