A brand new report highlights the demand for startups constructing open supply instruments and applied sciences for the snowballing AI revolution, with the adjoining knowledge infrastructure vertical additionally heating up.
Runa Capital, the enterprise capital (VC) agency that upped sticks from Silicon Valley and moved its HQ to Luxembourg in 2022, has revealed the Runa Open Supply Startup (ROSS) Index for the past four years, shining a light-weight on the fastest-growing commercial open source software (COSS) startups. The corporate publishes quarterly updates, nevertheless final 12 months it produced its first annual report taking a top-down view of the entire of 2022 — one thing it’s repeating now for 2023.
Developments
Information is intently aligned with AI as a result of AI depends on knowledge for studying and making predictions, and this requires infrastructure to handle the gathering, storage, and processing of that knowledge. And these tangential developments collided on this report.
Hitting top-spot within the ROSS Index for final 12 months was LangChain, a two-year-old San Francisco-based startup that has developed an open source framework for constructing apps primarily based on massive language fashions (LLMs). The corporate’s fundamental venture handed 72,500 stars in 2023, with Sequoia occurring to lead a $25 million Series A round into LangChain simply final month.
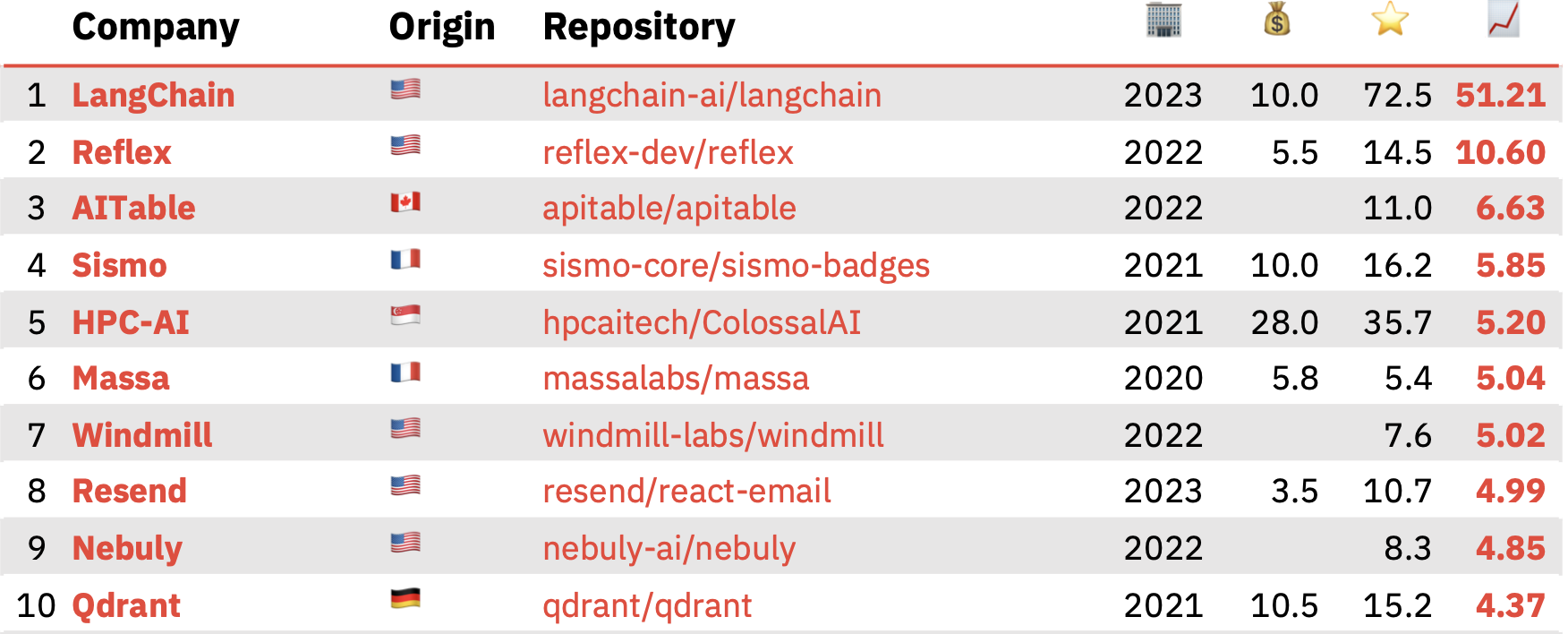
High 10 COSS startups within the ROSS Index for 2023 Picture Credit: Runa Capital
Elsewhere within the high 10 is Reflex, an open source framework for creating internet apps in pure Python, with the corporate behind the product just lately securing a $5 million seed funding; AITable, a spreadsheet-based AI chatbot builder and one thing akin to an open source Airtable competitor; Sismo, a privacy-focused platform that permits customers to selectively disclose personal data to purposes; HPC-AI, which is constructing a distributed AI improvement and deployment platform in a push to turn into one thing just like the OpenAI of Southeast Asia; and open supply vector database Qdrant, which recently secured $28 million to capitalize on the burgeoning AI revolution.
A broader take a look at the “top 50 trending” open supply startups final 12 months reveals that greater than half (26) are associated to AI and knowledge infrastructure.
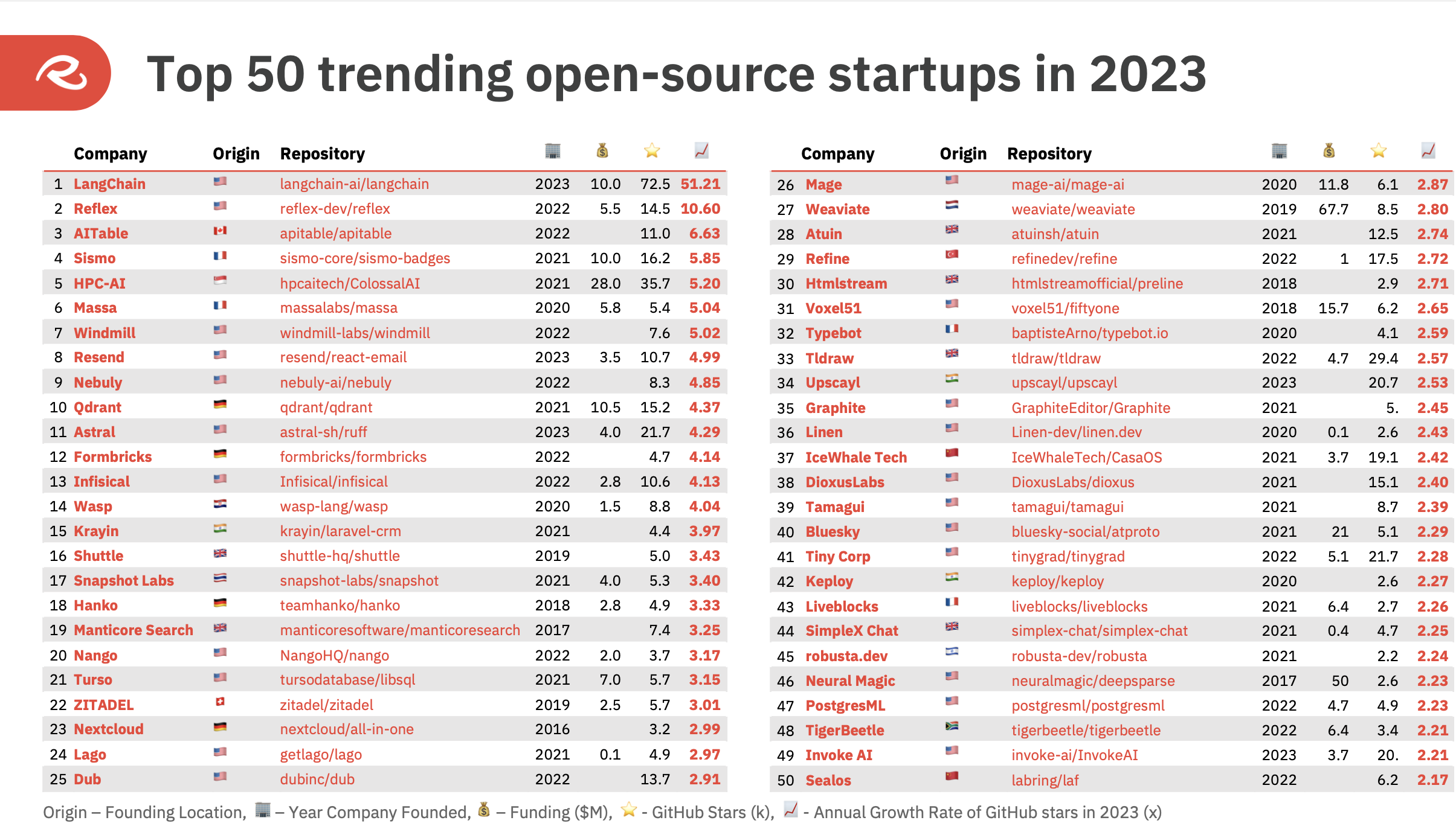

High 50 COSS startups within the ROSS Index for 2023 Picture Credit: Runa Capital
It’s tough to correctly evaluate the 2023 index with the earlier 12 months from a vertical perspective, due largely to the truth that companies usually pivot or change their product-positioning to go well with what’s scorching in the present day. With the ChatGPT hype train going full throttle final 12 months, this will have led earlier-stage startups to change their focus, and even simply place higher emphasis on the present “AI” factor of their product.
However as generative AI’s breakthrough year, it’s straightforward to see why demand for open-source componentry would possibly skyrocket, as corporations of all sizes look to maintain apace with proprietary AI juggernauts comparable to OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google.
Geographies
Open supply software program has additionally all the time been very distributed, with builders from everywhere in the world contributing. This ethos usually interprets into business open supply startups which could not have a conventional heart of gravity anchored by a brick-and-mortar HQ.
Nonetheless, the ROSS Index goes a way towards bringing geography into the image, reporting that 26 corporations on the checklist have an HQ within the U.S., although 10 of those corporations originated elsewhere and nonetheless have founders or workers primarily based in different locales.
In whole, the highest 50 hailed from 17 separate nations, with 23 of the businesses integrated in Europe — a 20% rise on the earlier 12 months’s index. France counted essentially the most COSS startups with seven, together with Sismo and Massa that are within the high 10, whereas the U.Okay. soared from only one startup in 2022 to 6 in 2023, putting it in second place from a European perspective.
Different notable tidbits to emerge from the report embrace programming languages — the ROSS Index recorded 12 languages utilized by the highest 50 final 12 months, versus 10 in 2022. However Typescript, a JavaScript superset developed by Microsoft, remained the preferred, utilized by 38% of the highest 50 startups. Each Python and Rust grew in recognition, with Go and JavaScript dropping.
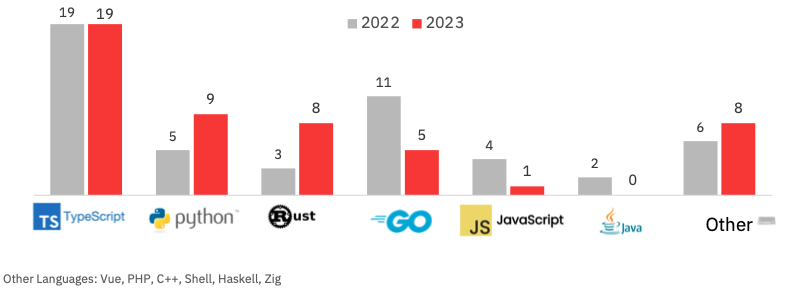

ROSS Index: Trending programming languages. Picture Credit: Runa Capital
The highest 50 ROSS Index contributors collectively gained 12,000 contributors in 2023, whereas the general GitHub star-count elevated by almost 500,000. The index additionally reveals that funding into the highest 50 COSS startups final 12 months hit $513 million, a rise of 32% on 2022 and 145% on 2021.
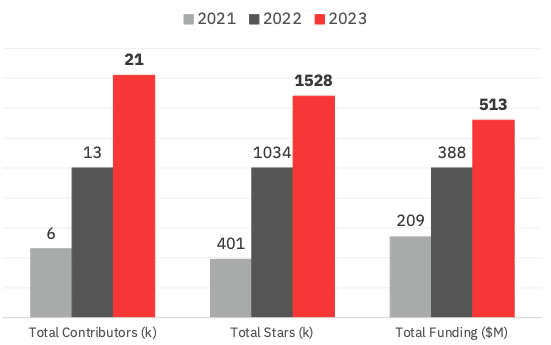

ROSS Index: Contributors, stars, and funding Picture Credit: Runa Capital
Methodology & context
It’s price trying on the methodology behind all this — what components affect whether or not an organization is taken into account “top trending”? For starters, all corporations included should have not less than 1,000 GitHub stars (a GitHub metric much like a “like” in social media) to be thought of. However star-count alone doesn’t inform us a lot about what’s trending, on condition that stars are accrued over time — so a venture that has been on GitHub for 10 years is more likely to have accrued extra stars than one which has existed for 10 months. As a substitute, Runa measures the relative progress of the celebrities over a given interval utilizing an annualised progress charge (AGR) — this seems to be on the star worth now versus a earlier corresponding interval to see what has grown most impressively.
A level of handbook curation is concerned right here, too, on condition that the objective is to eke out open supply “startups” particularly — so the Runa funding workforce pulls out initiatives that belong to a “product-focused commercial organization,” and it has to have been based fewer than ten years in the past with lower than $100 million in identified funding.
Defining what constitutes “open source” has its personal inherent challenges too, as there’s a spectrum of how “open source” a startup is — some are extra akin to “open core,” the place most of their main options are locked behind a premium paywall, and a few have licenses that are extra restrictive than others. So for this, the curators at Runa determined that the startup should merely have a product that’s “reasonably connected to its open-source repositories,” which clearly entails a level of subjectivity when deciding which of them make the reduce.
There are additional nuances at play too. The ROSS Index adopts a very liberal interpretation of “open source” — for instance, both Elastic and MongDB abandoned their open source roots for licenses which are “source available,” to guard themselves from being taken benefit of by the key cloud suppliers. In response to the ROSS Index’s methodology, each these corporations would qualify as “open source” — regardless that their licenses will not be formally authorized as such by the Open Source Initiative, and these particular instance corporations now not seek advice from themselves as “open source.”
Thus, in line with Runa’s methodology, it makes use of what it calls the “commercial perception of open-source” for its report, quite than the precise license the corporate attaches to its venture. Which means restricted source-available licenses like BSL (enterprise supply license) and SSPL (server facet public license), which MongoDB launched as a part of its transition away from open supply in 2018, are very a lot on the menu so far as business corporations within the ROSS Index is anxious.
“Such licenses maintain the OSS spirit — all its freedoms, except for slightly limited redistribution, which does not affect developers but grants original vendors a long-term competitive edge,” Konstantin Vinogradov, Runa Capital’s London-based common associate, defined to TechCrunch. “From a VC perspective, it is just an evolved playbook for exactly the same type of companies. The open source definition applies to software products, not companies.”
There are different notable filters in place too. As an illustration, corporations which are principally centered on offering skilled companies, or side-projects with restricted lively assist or with no business factor, will not be included within the ROSS Index.
For comparative functions, there are different indexes and lists on the market that give a steer on the “whats hot” within the open supply panorama. One other VC agency referred to as Two Sigma Ventures maintains the Open Source Index, for example, which is analogous in idea to Runa’s, besides it spans all method of open supply initiatives (not simply startups) and has further filters in place, together with the power to view by GitHub’s “watchers” metric, which some argue offers a extra correct image of a venture’s true recognition.
GitHub itself additionally publishes a trending repositories web page, which much like Two Sigma Ventures, doesn’t give attention to the enterprise behind the venture.
So the ROSS Index has emerged as a helpful complementary instrument for determining which open supply “startups” particularly are price maintaining tabs on.















