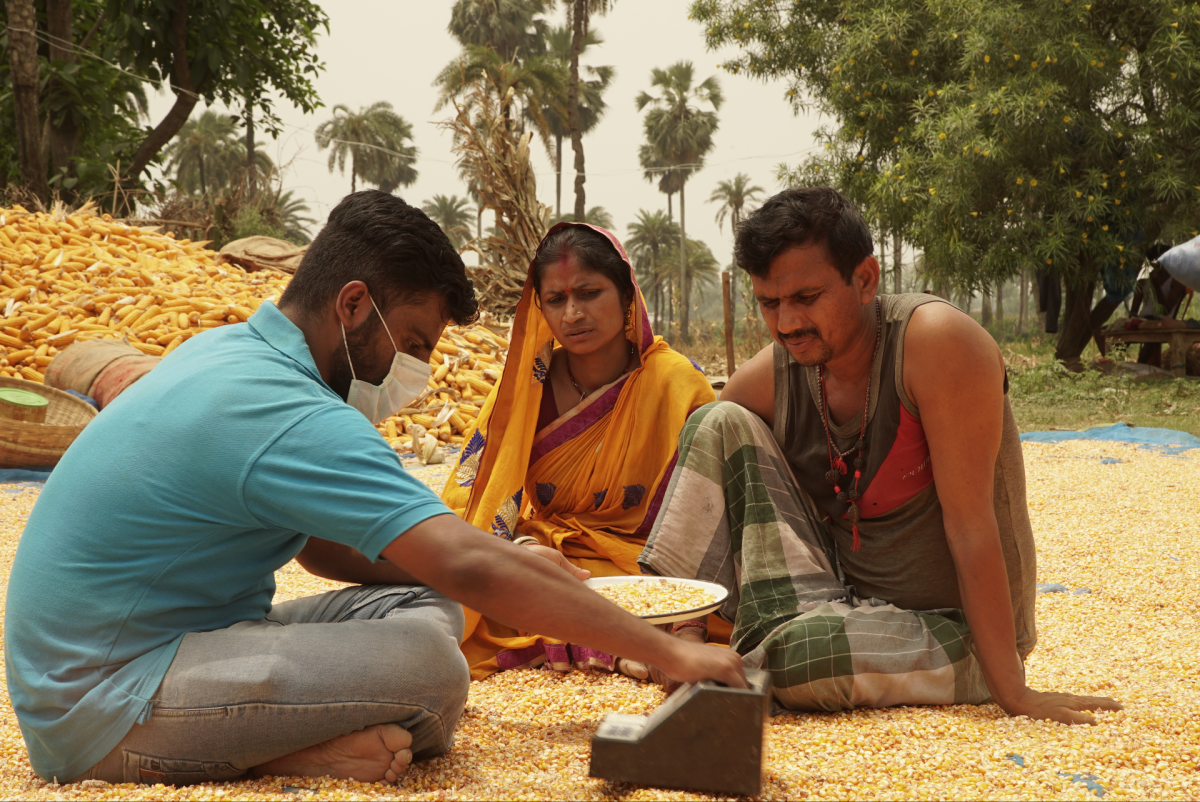
Arya.ag, an Indian agritech company offering storage facilities near farms and offering lending services to hundreds of thousands of farmers, has drawn investor interest and remained profitable even as global crop prices continue to fall in a volatile commodities market.
The investor interest has taken shape in the latest all-equity Series D round from GEF Capital Partners, totaling $81 million, of which more than 70% was primary capital and the rest secondary share sales, according to the company.
Globally, agricultural commodity prices are falling. Risks from extreme weather, input costs, trade disruptions, and biofuel policy shifts continue to weigh on agricultural markets, the World Bank has warned. This leaves businesses exposed to price swings and inventory losses. Nonetheless, Arya.ag says it is navigating the worst of that strain by steering clear of direct commodity bets and using a model that it says helps absorb shocks from downward pricing shifts.
Founded in 2013 by former ICICI Bank executives Prasanna Rao, Anand Chandra, and Chattanathan Devarajan, Arya.ag is built around a simple idea: giving farmers more control over when and to whom they sell their crops. The Noida-based startup offers storage close to farms while allowing farmers to borrow against warehoused grain to meet immediate cash needs and connecting them with a wider pool of buyers — from agri-corporations to processors and millers — helping them avoid the pressure to sell just after harvest, when prices are often weakest.
The company operates at scale, which sets Arya.ag apart from traditional lenders, banks, and other agribusiness platforms. The startup says it aggregates and stores about $3 billion worth of grain each year — roughly 3% of national output — and facilitates around $1.5 billion in loans annually, while keeping its rate of bad loans (known as gross non-performing assets, or NPAs) below 0.5% despite the recent drop in prices.
Arya.ag lends only a portion of the value of stored grain and tracks prices closely, triggering margin calls when required rather than taking losses itself, Rao said. Borrowers can respond by repaying part of the loan or adding more grain as collateral.
“You’re not immune to risks,” Rao told TechCrunch. “But because your lending is completely secured against commodities, it will never happen that the prices will fall by 90%. You already have a margin of 30%, and with your mark to market, you’ve been able to control your NPAs and defaults.”
Techcrunch event
San Francisco
|
October 13-15, 2026
In the year ended March 2025, Arya.ag generated net revenue of ₹4.5 billion (around $50 million), with first-half revenue in the current financial year rising about 30% from a year earlier to ₹3 billion ($33.3 million). Profit after tax stood at ₹340 million (about $3.78 million) last year, and has risen a further 39% so far this year, Rao said.

Arya.ag says it now reaches between 850,000 and 900,000 farmers across 60% of India’s districts, operating through a network of about 12,000 agricultural warehouses, all leased from third parties. The startup generates revenue from farmers for storage, from banks for originating loans against stored grain, and from buyers for facilitating crop sales through its platform.
Storage remains the largest contributor, accounting for about 50–55% of total revenue, while finance contributes 25–30% and the rest comes from commerce, Rao said.
Arya.ag disburses more than ₹110 billion (about $1.2 billion) in loans to farmers each year through its platform. Between ₹25 billion and ₹30 billion (roughly $278 million–$333 million) of that comes from its own balance sheet via its non-banking finance arm, Rao said, with the rest originated for partner banks.
Arya.ag’s loans carry interest rates of about 12.5% to 12.8%, well below the 24% to 36% typically charged by commission agents, Rao said, though higher than bank lending rates of around 11% to 12%. He added that banks generally do not lend in the small, local markets close to farming areas that Arya serves, where loan sizes are a fraction of typical bank tickets and borrowers are often located far from formal branches.
The startup approves loans in under five minutes with disbursements handled almost entirely digitally, Rao said.
Technology plays a central role in how Arya.ag manages risk and scale. The startup uses AI to assess grain quality for lending decisions, satellite data to track crop stress before harvest, and airtight, sensor-enabled storage bags that allow farmers to store grain for extended periods even in villages without formal warehouses.
Arya.ag plans to use the fresh capital to scale its tech deployments further, including expanding smart farm centers and deploying more digital tools closer to farms. Part of the investment, Rao said, will also go toward strengthening the startup’s blockchain-based system that digitally tracks stored grain, allowing crops used as collateral or sold through the platform to be monitored across lending and trade transactions, alongside continued investment in storage and credit infrastructure.
With the latest capital infusion and improving profitability, Arya.ag is aiming to be IPO-ready in the next 18 to 20 months, Rao said.
Beyond India, Arya.ag plans to expand selectively through a software-led model, with some of its technology already deployed in parts of Southeast Asia and Africa. The startup has a headcount of over 1,200 full-time employees.
Avendus advised Arya.ag for the new financial round.