What’s the following huge factor in enterprise automation? Should you ask the tech giants, it’s brokers — pushed by generative AI.
There’s no universally accepted definition of agent, however lately the time period is used to explain generative AI-powered instruments that may carry out advanced duties via human-like interactions throughout software program and internet platforms.
For instance, an agent may create an itinerary by filling in a buyer’s information on airways’ and resort chains’ web sites. Or an agent may order the least costly ride-hailing service to a location by mechanically evaluating costs throughout apps.
Distributors sense alternative. ChatGPT maker OpenAI is reportedly deep into growing AI agent techniques. And Google demoed a slew of agent-like merchandise at its annual Cloud Subsequent convention in early April.
“Companies should start preparing for wide-scale adoption of autonomous agents today,” analysts at Boston Consulting Group wrote not too long ago in a report — citing specialists who estimate that autonomous brokers will go mainstream in three to 5 years.
Previous-school automation
So the place does that go away RPA?
Robotic course of automation (RPA) got here into vogue over a decade in the past as enterprises turned to the tech to bolster their digital transformation efforts whereas lowering prices. Like an agent, RPA drives workflow automation. But it surely’s a way more inflexible kind, based mostly on “if-then” preset guidelines for processes that may be damaged down into strictly outlined, discretized steps.
“RPA can mimic human actions, such as clicking, typing or copying and pasting, to perform tasks faster and more accurately than humans,” Saikat Ray, VP analyst at Gartner, defined to TechCrunch in an interview. “However, RPA bots have limitations when it comes to handling complex, creative or dynamic tasks that require natural language processing or reasoning skills.”
This rigidity makes RPA costly to construct — and significantly limits its applicability.
A 2022 survey from Robocorp, an RPA vendor, finds that of the organizations that say they’ve adopted RPA, 69% expertise damaged automation workflows not less than as soon as per week — lots of which take hours to repair. Entire businesses have been made out of serving to enterprises handle their RPA installations and forestall them from breaking.
RPA distributors aren’t naive. They’re properly conscious of the challenges — and imagine that generative AI may resolve lots of them with out hastening their platforms’ demise. In RPA distributors’ minds, RPA and generative AI-powered brokers can peacefully co-exist — and maybe sooner or later even develop to enhance one another.
Generative AI automation
UiPath, one of many bigger gamers within the RPA market with an estimated 10,000+ prospects, together with Uber, Xerox and CrowdStrike, not too long ago introduced new generative AI options targeted on doc and message processing, in addition to taking automated actions to ship what UiPath CEO Bob Enslin calls “one-click digital transformation.”
“These features provide customers generative AI models that are trained for their specific tasks,” Enslin instructed TechCrunch. “Our generative AI powers workloads such as text completion for emails, categorization, image detection, language translation, the ability to filter out personally identifiable information [and] quickly answering any people-topic-related questions based off of knowledge from internal data.”
One in every of UiPath’s more moderen explorations within the generative AI area is Clipboard AI, which mixes UiPath’s platform with third-party fashions from OpenAI, Google and others to — as Enslin places it — “bring the power of automation to anyone that has to copy/paste.” Clipboard AI lets customers spotlight knowledge from a kind, and — leveraging generative AI to determine the precise locations for the copied knowledge to go — level it to a different kind, app, spreadsheet or database.
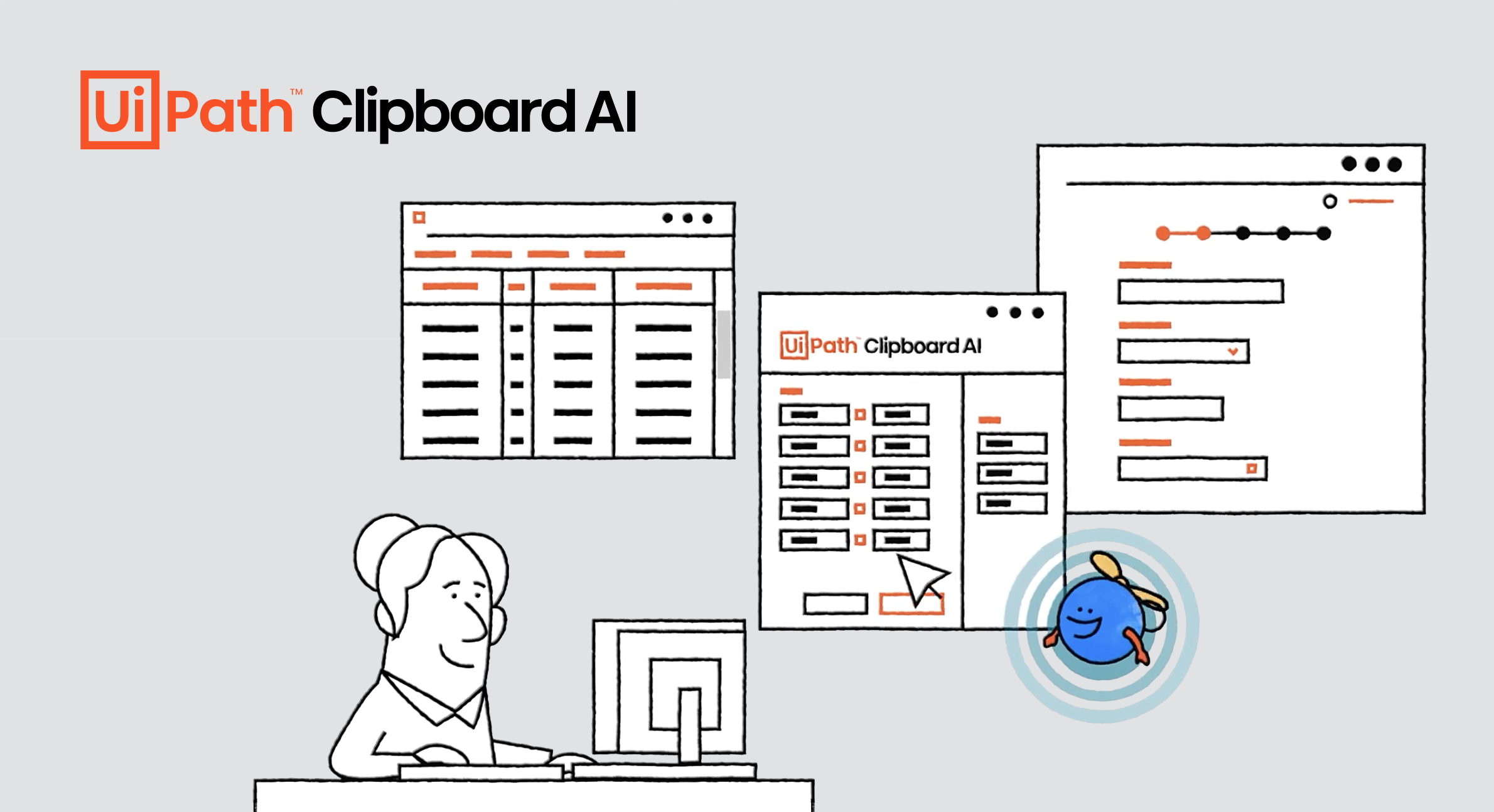
Picture Credit: UiPath
“UiPath sees the need to bring action and AI together; this is where value is created,” Enslin mentioned. “We believe the best performance will come from those that combine generative AI and human judgment — what we call human-in-the-loop — across end-to-end processes.”
Automation Wherever, UiPath’s essential rival, can also be making an attempt to fold generative AI into its RPA applied sciences.
Final yr, Automation Wherever launched generative AI-powered instruments to create workflows from pure language, summarize content material, extract knowledge from paperwork and — maybe most importantly — adapt to adjustments in apps that will usually trigger an RPA automation to fail.
“[Our generative AI models are] developed on top of [open] large language models and trained with anonymized metadata from more than 150 million automation processes across thousands of enterprise applications,” Peter White, SVP of enterprise AI and automation at Automation Wherever, instructed TechCrunch. “We continue to build custom machine learning models for specific tasks within our platform and are also now building customized models on top of foundational generative AI models using our automation datasets.”
Subsequent-gen RPA
Ray notes it’s necessary to be cognizant of generative AI’s limitations — specifically biases and hallucinations — because it powers a rising variety of RPA capabilities. However, dangers apart, he believes generative AI stands so as to add worth to RPA by remodeling the way in which these platforms work and “creating new possibilities for automation.”
“Generative AI is a powerful technology that can enhance the capabilities of RPA platforms enabling them to understand and generate natural language, automate content creation, improve decision-making and even generate code,” Ray mentioned. “By integrating generative AI models, RPA platforms can offer more value to their customers, increase their productivity and efficiency and expand their use cases and applications.”
Craig Le Clair, principal analyst at Forrester, sees RPA platforms as being ripe for enlargement to help autonomous brokers and generative AI as their use instances develop. In truth, he anticipates RPA platforms morphing into all-around toolsets for automation — toolsets that assist deploy RPA along with associated generative AI applied sciences.
“RPA platforms have the architecture to manage thousands of task automations and this bodes well for central management of AI agents,” he mentioned. “Thousands of companies are well established with RPA platforms and will be open to using them for generative AI-infused agents. RPA has grown in part thanks to its ability to integrate easily with existing work patterns, through UI integration, and this will remain valuable for more intelligent agents going forward.”
UiPath is already starting to take steps on this path with a brand new functionality, Context Grounding, that entered preview earlier within the month. As Enslin defined it to me, Context Grounding is designed to enhance the accuracy of generative AI fashions — each first- and third-party — by changing enterprise knowledge these fashions would possibly draw on into an “optimized” format that’s simpler to index and search.
“Context Grounding extracts information from company-specific datasets, like a knowledge base or internal policies and procedures, to create more accurate and insightful responses,” Enslin mentioned.
If there’s something holding RPA distributors again, it’s the ever-present temptation to lock prospects in, Le Clair mentioned. He confused the necessity for platforms to “remain agnostic” and supply instruments that may be configured to work with a spread of present — and future — enterprise techniques and workflows.
To that, Enslin pledged that UiPath will stay “open, flexible and responsible.”
“The future of AI will require a combination of specialized AI with generative AI,” he continued. “We want customers to be able to confidently use all kinds of AI.”
White didn’t decide to neutrality precisely. However he emphasised that Automation Wherever’s roadmap is being closely formed by buyer suggestions.
“What we hear from every customer, across every industry, is that their ability to incorporate automation in many more use cases has increased exponentially with generative AI,” he mentioned. “With generative AI infused into intelligent automation technologies like RPA, we see the potential for organizations to reduce operating costs and increase productivity. Companies who fail to adopt these technologies will struggle to compete against others who embrace generative AI and automation.”