A measure of inflation that’s carefully tracked by the Federal Reserve slipped final month in an indication that value pressures proceed to ease.
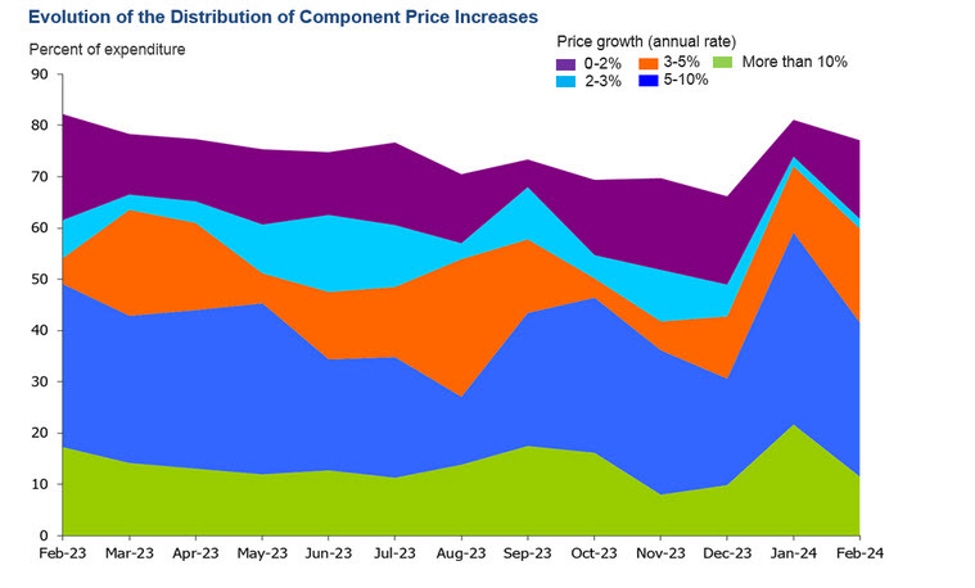
The federal government reported Friday that costs rose 0.3% from January to February, decelerating from a 0.4% enhance the earlier month in a doubtlessly encouraging pattern for President Joe Biden’s re-election bid. In contrast with 12 months earlier, although, costs rose 2.5% in February, up barely from a 2.4% year-over-year achieve in January.
Excluding unstable meals and power prices, final month’s “core” costs urged decrease inflation pressures. These costs rose 0.3% from January to February, down from 0.5% the earlier month. And core costs rose simply 2.8% from 12 months earlier — the bottom such determine in almost three years — down from 2.9% in January. Economists think about core costs to be a greater gauge of the seemingly path of future inflation.
Friday’s report confirmed {that a} sizable soar in power costs — up 2.3% — boosted the general costs of products by 0.5% in February. Against this, inflation in providers — an enormous vary of things starting from lodge rooms and restaurant meals to healthcare and live performance tickets — slowed to a 0.3% enhance, from a 0.6% rise in January.
The figures additionally revealed that buyers, whose purchases drive a lot of the nation’s financial development, surged 0.8% final month, up from a 0.2% achieve in January. A few of that enhance, although, mirrored increased gasoline costs.
Annual inflation, as measured by the Fed’s most popular gauge, tumbled in 2023 after having peaked at 7.1% in mid-2022. Supply chain bottlenecks eased, lowering the prices of supplies, and an influx of job seekers made it simpler for employers to maintain a lid on wage development, one of many drivers of inflation.
Nonetheless, inflation stays stubbornly above the Fed’s 2% annual goal, and opinion surveys have revealed public discontent that top costs are squeezing America’s households regardless of a pointy pickup in common wages.
The acceleration of inflation started within the spring of 2021 because the economic system roared again from the pandemic recession, overwhelming factories, ports and freight yards with orders. In March 2022, the Fed started elevating its benchmark rate of interest to attempt to sluggish borrowing and spending and funky inflation, finally boosting its charge 11 instances to a 23-year excessive. These sharply increased charges labored as anticipated in serving to tame inflation.
The soar in borrowing prices for corporations and households was additionally anticipated, although, to trigger widespread layoffs and tip the economic system right into a recession. That didn’t occur. The economy has grown at a healthy annual rate of two% or extra for six straight quarters. Job growth has been solid. And the unemployment charge has remained beneath 4% for 25 straight months, the longest such streak for the reason that Sixties.
The mixture of easing inflation and durable development and hiring has raised expectations that the Fed will obtain a troublesome “soft landing″ — taming inflation with out inflicting a recession. If inflation continues to ease, the Fed will seemingly start reducing its key charge within the coming months. Fee cuts would, over time, result in decrease prices for residence and auto loans, bank card borrowing and enterprise loans. They may additionally assist Biden’s re-election prospects.
Michael Pearce, economist at Oxford Economics, stated that even a 0.3% January-to-February uptick in client costs was in all probability nonetheless too scorching for the Fed’s inflation fighters. The central financial institution has signaled that it expects to chop charges 3 times this 12 months, and Wall Road buyers have been eagerly awaiting the transfer. Pearce wrote {that a} June charge reduce now seems to be extra seemingly than the Might reduce that he and his Oxford colleagues had beforehand anticipated.
The Fed tends to favor the inflation gauge that the federal government issued Friday — the private consumption expenditures value index — over the better-known consumer price index. The PCE index tries to account for modifications in how individuals store when inflation jumps. It might probably seize, for instance, when shoppers change from pricier nationwide manufacturers to cheaper retailer manufacturers.
On the whole, the PCE index tends to point out a decrease inflation degree than CPI. Partly, that’s as a result of rents, which have been excessive, carry double the burden within the CPI that they do within the PCE.
Friday’s authorities report confirmed that Individuals’ incomes rose 0.3% in February, down sharply from a 1% achieve in January, which had been boosted by once-a-year cost-of-living will increase in Social Safety and different authorities advantages.