Whats up and welcome again to TechCrunch Area. What every week! For the second week in a row, we’ve got lunar lander information to report on. Plus, a ultimate replace on Astrobotic’s Peregrine lander, information on the Artemis program and the primary crewed launch of the yr.
Wish to attain out with a tip? Electronic mail Aria at [email protected] or ship me a message on Sign at 512-937-3988. You can too ship a notice to the entire TechCrunch crew at [email protected]. For safer communications, click here to contact us, which incorporates SecureDrop (instructions here) and hyperlinks to encrypted messaging apps.
Story of the week
How may the story of the week be something aside from SLIM (Good Lander for Investigating Moon), the Japanese lunar lander that touched down on the moon on Friday?
This makes Japan the fifth nation to place a lander on the moon, becoming a member of the ranks of america, China, Russia and India. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) confirmed that they’d acquired telemetry knowledge from SLIM simply after 10:20 AM EST.
Whereas the touchdown was successful, not all went to plan, sadly: JAXA later said that the lander’s photo voltaic cells aren’t at the moment producing electrical energy, which implies that the mission lifetime shall be tremendously lowered. There’s a small probability that the photo voltaic cells may cost because the angle of the solar modifications, however that depends upon whether or not the trigger is because of a pointing challenge or another anomaly, JAXA officers mentioned in a press convention.
However even with the difficulty, the mission achieved an enormous portion of its objective, which was to show a delicate lunar touchdown utilizing optical navigation expertise. This new sort of expertise may help guarantee “pinpoint” landings, or landings with an accuracy of round 100 meters, versus many kilometers.
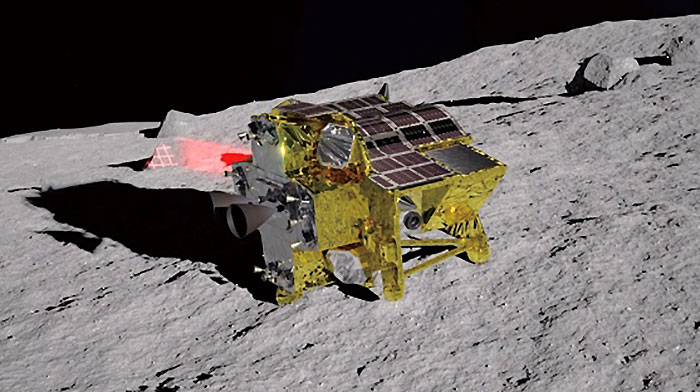
Picture Credit: Japan Aerospace Exploration Company
Launch highlights
We noticed our first crewed mission this yr – however much more notably, it was a totally non-public mission (as in not a NASA astronaut mission). Axiom Space launched its third mission with launch partner SpaceX on Thursday, with the crew efficiently docking with the Worldwide Area Station at 5:42 AM EST on Saturday, January 20.
Axiom’s plan is to proceed flying these non-public missions to the ISS at a tempo of round two missions per yr by means of 2026, which is when the corporate hopes to launch its first industrial area station module, Derek Hassmann, chief of mission integration and operations at Axiom Area, mentioned throughout a prelaunch press convention. Axiom’s fourth flight, Ax-4, is scheduled for later this yr, although a selected launch window has not been introduced.
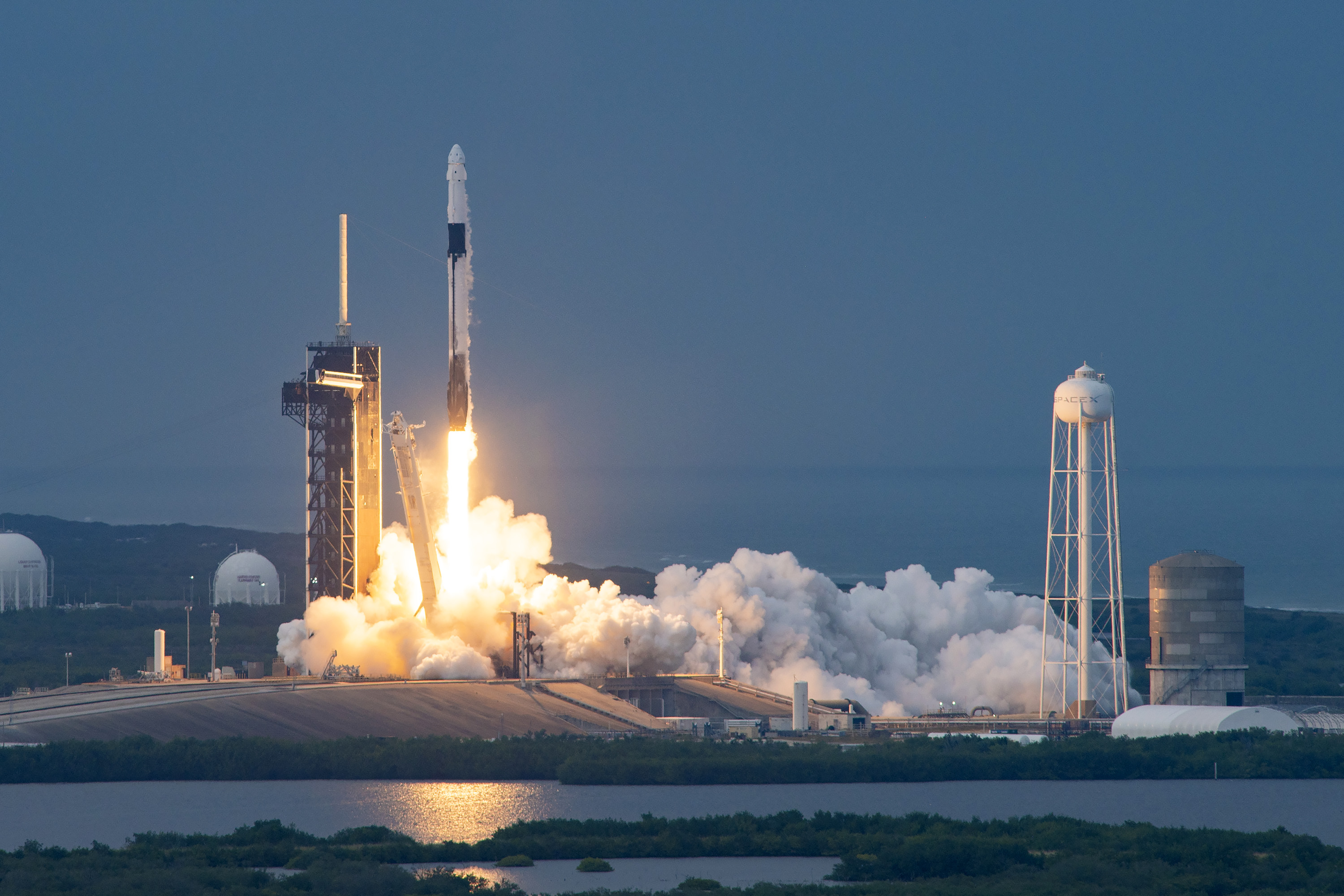


Picture credit score: SpaceX
What we’re studying
Loren Grush very nicely lays out a few of NASA’s forward-thinking technique with its Industrial Lunar Payload Providers (CLPS) program: settle for some threat. This system was established to assist kickstart the event of payload supply surfaces to the moon’s floor, and it stands in sharp distinction to NASA’s customary quo.
Astrobotic’s Peregrine lander, which suffered a deadly propulsion leak that prevented the spacecraft from having any probability of touchdown on the moon, is the results of a CLPS award. Whereas Astrobotic didn’t full the mission, Grush describes how NASA designed this system to be extra risk-tolerant than its different endeavors.
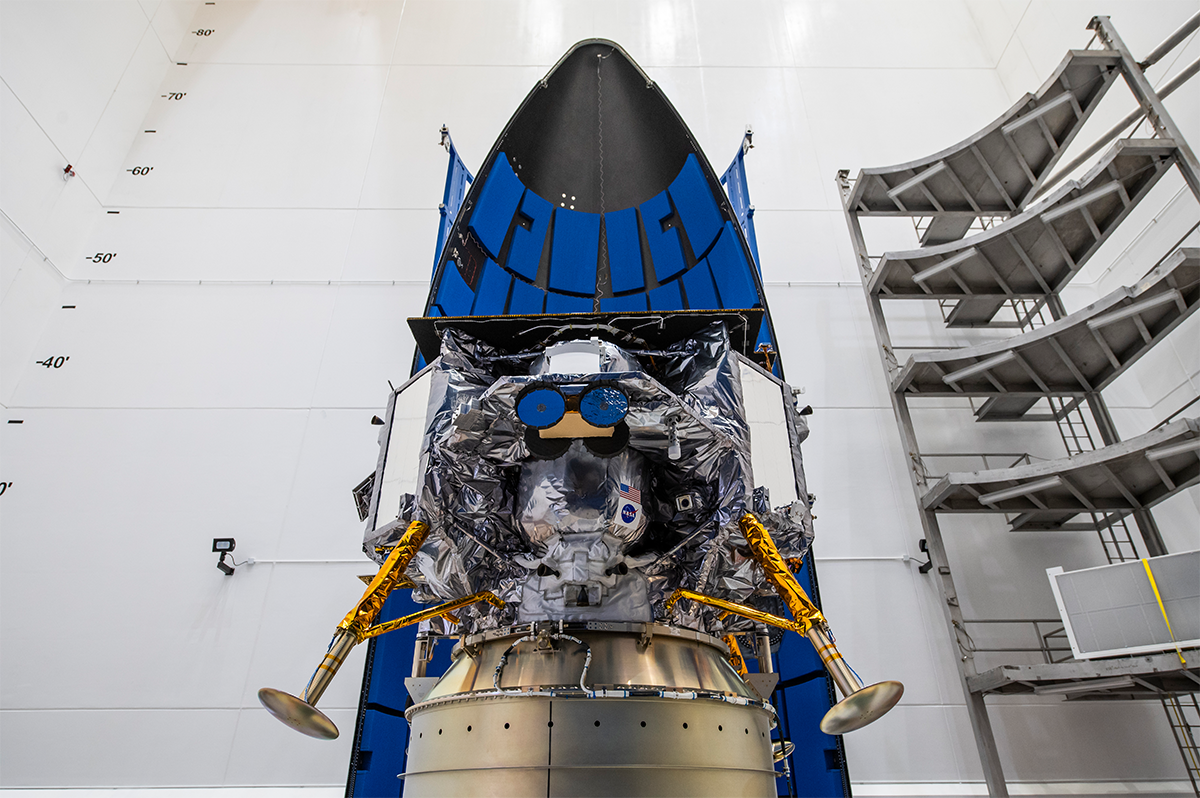

Astrobotic Peregrine Lunar Lander
This week in area historical past
Thirty-two years in the past this week, microgravity analysis was born. In 1992, NASA launched the primary Worldwide Microgravity Laboratory on board the area shuttle Discovery, and it carried quite a few scientific analysis and experiments trying into the consequences of zero G on supplies and residing organisms. The lab was pressurized, so the mission additionally carried a crew of seven; they returned to Earth after eight days in area.
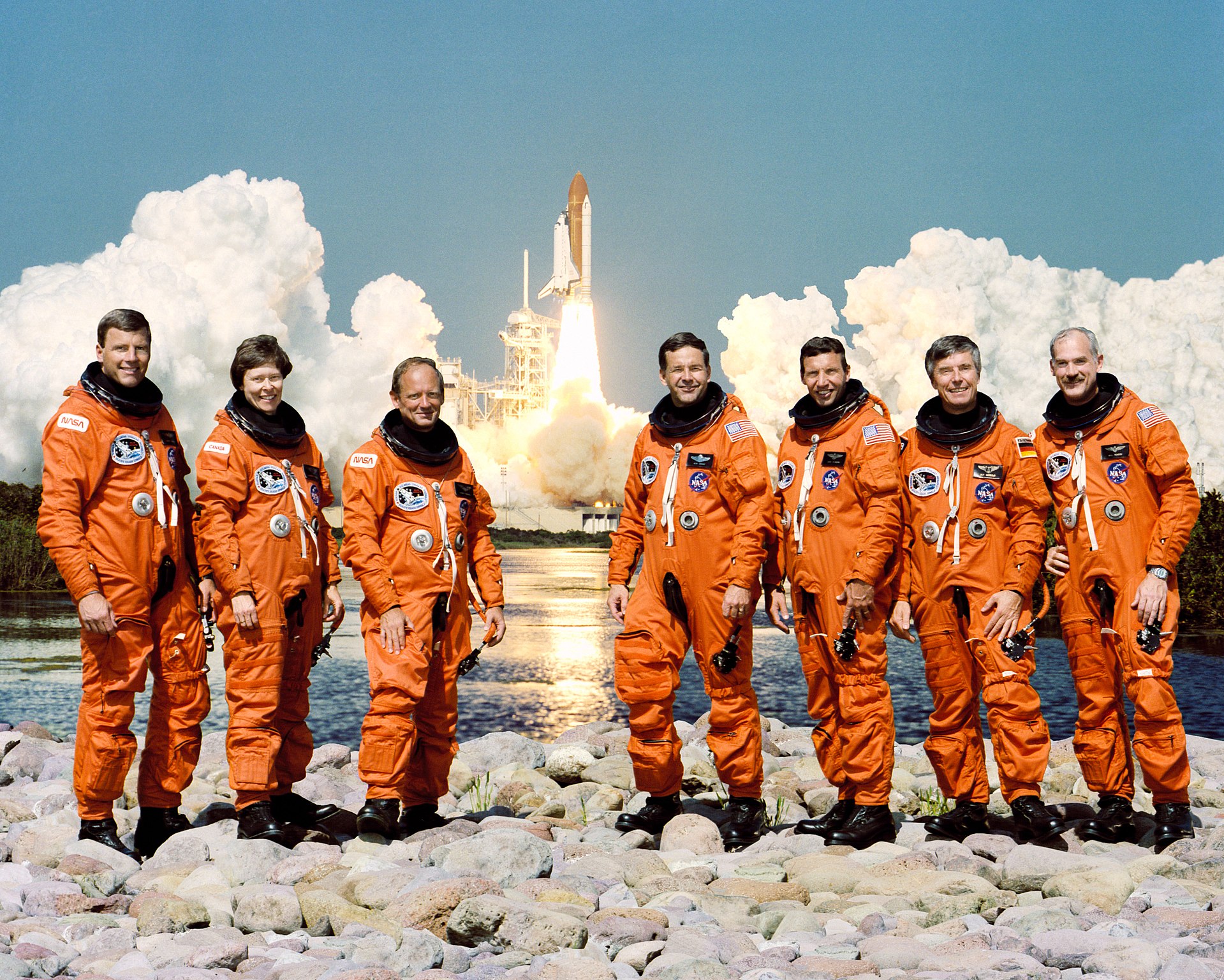


Picture credit score: NASA