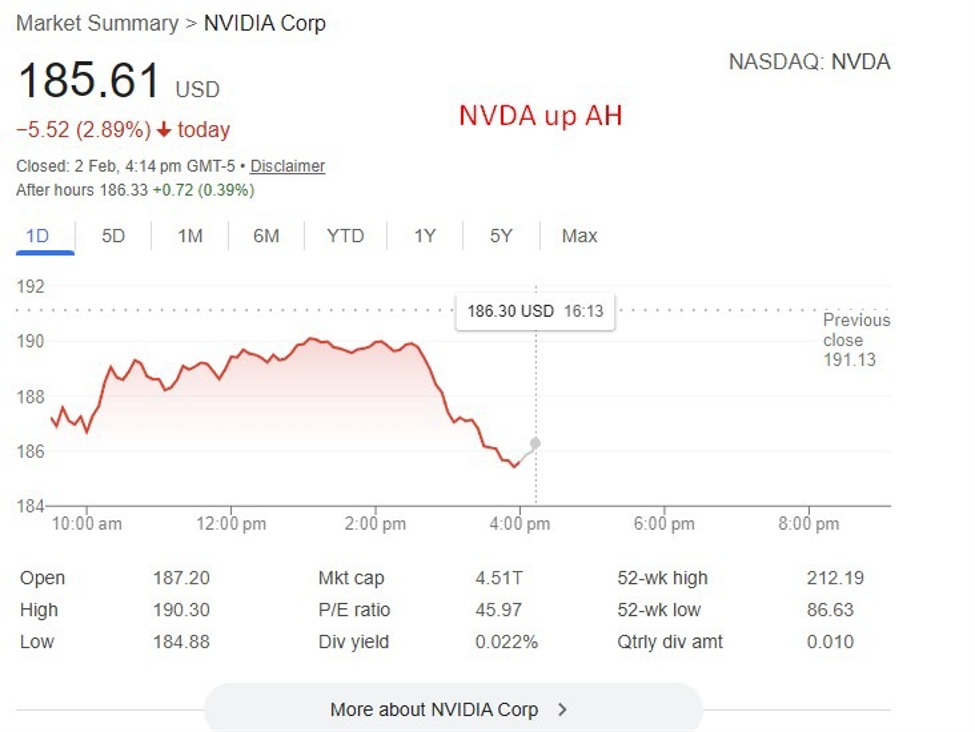
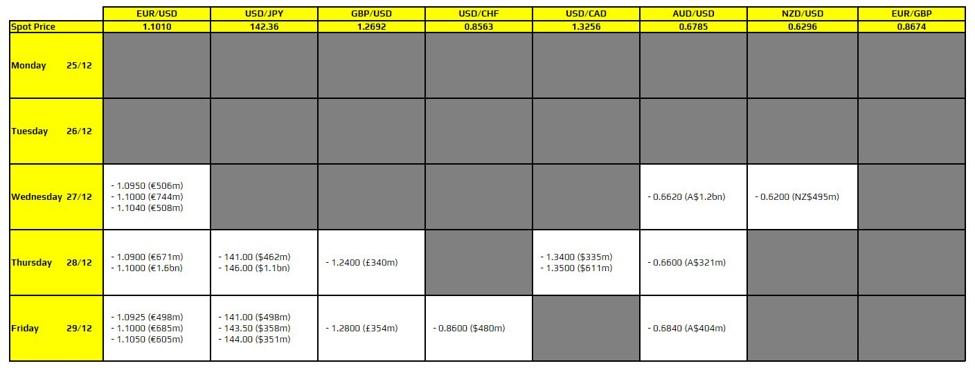
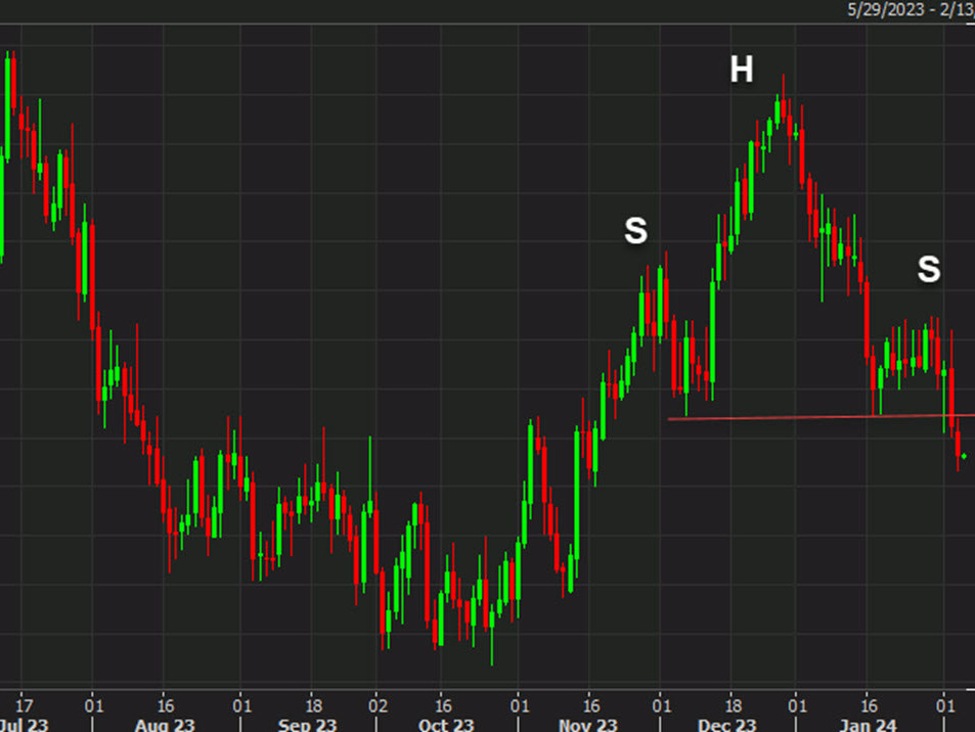
OpenAI’s reported chip review highlights mounting pressure on AI hardware vendors as inference speed and efficiency become critical competitive battlegrounds.
Summary:
-
OpenAI is assessing alternatives to Nvidia’s latest AI chips for some workloads
-
Review has been underway since last year, according to sources
-
Focus is on inference speed for complex ChatGPT queries
-
Reflects rising pressure to optimise latency and throughput at scale
-
Signals broader push to diversify AI hardware dependence
OpenAI is actively exploring alternatives to Nvidia’s latest AI chips in certain use cases, according to sources familiar with the matter, reflecting growing performance and scaling challenges as demand for advanced AI services accelerates.
Sources indicate OpenAI has been assessing non-Nvidia hardware options since last year, driven in part by dissatisfaction with the speed at which current-generation Nvidia accelerators can deliver responses to users for more complex queries. While Nvidia’s GPUs remain central to large-scale AI training and inference, the issue appears less about absolute capability and more about efficiency, latency and throughput as models grow larger and workloads become increasingly demanding.
The push highlights a broader industry challenge: as generative AI adoption expands, the bottleneck is shifting from model development to real-time inference performance. For consumer-facing products such as ChatGPT, even marginal delays in generating responses can have material implications for user experience, operating costs and scalability.
OpenAI’s exploration of alternatives does not necessarily imply an imminent shift away from Nvidia, which continues to dominate the AI accelerator market. Instead, the move suggests a desire to diversify hardware exposure, reduce reliance on a single supplier and potentially optimise different workloads across multiple chip architectures.
The development comes amid intensifying competition across the AI hardware landscape, with several chipmakers and cloud providers racing to offer specialised accelerators aimed at faster inference, lower power consumption and improved cost efficiency. For Nvidia, the report underscores the growing scrutiny facing its hardware roadmap as customers move from experimental AI deployment toward mass-market, latency-sensitive applications.
Markets are likely to view the story less as a near-term revenue risk for Nvidia and more as a signal that the next phase of AI competition will be defined by performance-per-dollar and response speed, rather than raw training power alone.