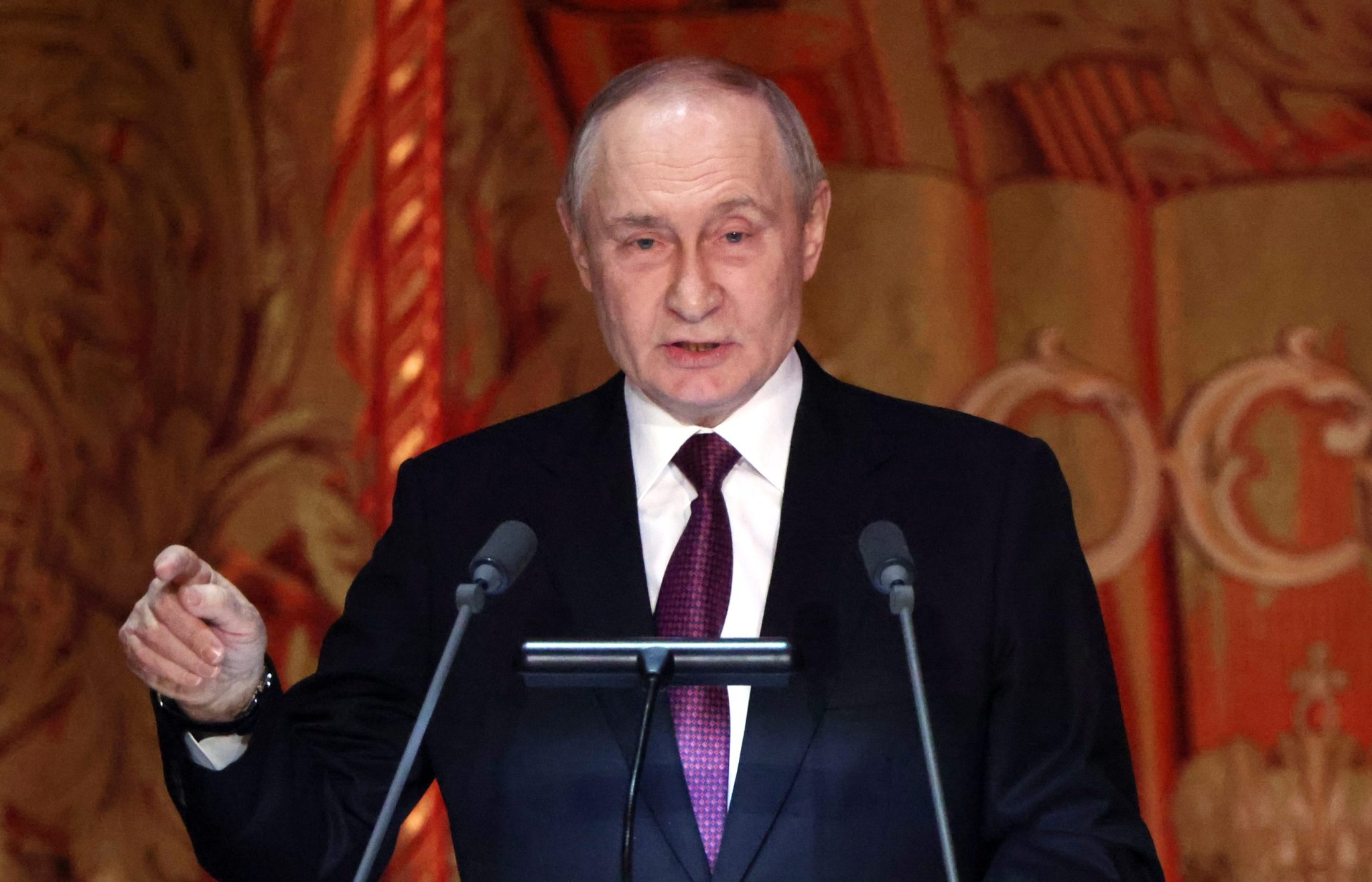
Vladimir Putin’s wartime economy has been resilient in the face of Western sanctions triggered by his invasion of Ukraine, but it’s hitting a wall and U.S. pressure on the energy sector could cause a recession, according to experts.
Massive defense spending has propped up growth, kept factories humming, and pushed unemployment lower, while Moscow has relied on allies like China for goods no longer available from the West.
“But the country has exhausted its reserves of manufacturing capacity and manpower,” Alexandra Prokopenko, a fellow at the Carnegie Russia Eurasia Center and former Russian central bank advisor, wrote in Foreign Affairs on Monday.
“To produce substantially more equipment or recruit and train far more soldiers, Moscow would have to shift to a more comprehensive war footing by directing all available resources toward military needs, as it did during World War II, or commandeering civilian production lines for military purposes.”
Such a mobilization would require Moscow to order car plants, for example, to exclusively produce military vehicles. But the Russian government hasn’t resorted to those measures because it doesn’t want to create shortages of consumer goods and risk social unrest, she added.
Meanwhile, production bottlenecks, labor shortages, tighter government spending, and the lack of Western technology are increasingly causing strains in the economy, Prokopenko said.
GDP growth is slowing sharply, tracking at just 1.1% so far this year, down from 4.1% in 2024 and 3.6% in 2023. That’s partly because all the money Moscow spends for its war on Ukraine has few lasting benefits.
“In effect, defense spending functions like a disposable-goods economy: factories operate at full capacity, workers earn wages, and demand for inputs surges, but the output is designed to vanish almost immediately,” she explained.
Not only do weapons and equipment get obliterated on the battlefield, but payments for dead and injured soldiers will continue to weigh on the Kremlin’s budget even after the fighting ends.
Such spending contrasts with government outlays on infrastructure that help improve an economy’s long-term potential.
“This cycle sustains employment and industrial activity in the short term but generates no lasting assets—such as highways, power plants, or schools—or productivity gains, leaving the economy busier yet poorer with each passing year of war,” Prokopenko wrote.
Russian recession warnings
And U.S. sanctions announced Wednesday on Russian energy giants Rosneft and Lukoil could push the economy over the edge.
That’s as oil and gas revenue, which is the Kremlin’s main source of funds, has been falling amid low energy prices, forcing Russia to rein in its budget. The two companies account for about half of the country’s oil exports, and Rosneft alone contributes about 17% of Russia budget revenue.
While they can still find ways to sell their crude, it will require more work-arounds that add to costs while some customers may balk over fears of secondary sanctions.
“As for Russia itself, the hit to energy revenues could tip the economy into recession,” Capital Economics said in a note on Thursday.
It’s possible a recession has already arrived. Last month, data from Russia’s central bank showed GDP shrank on a sequential basis in the first and second quarters, meeting the definition of a so-called technical recession.
Also last month, Sberbank CEO German Gref, one of Russia’s top banking chiefs, said the economy was in “technical stagnation,” And in June, Economy Minister Maxim Reshetnikov warned that Russia was “on the brink” of a recession.
To be sure, much depends on U.S. execution of its new sanctions, while markets weigh whether the measures are another example of President Donald Trump’s negotiating strategy of escalating to de-escalate.
Indeed, Capital Economics said it’s hard to see Trump sticking with a policy that would raise U.S. gasoline prices.
But even if Russia suffers a recession, analysts see a low probability that it will be enough to bring Putin to the negotiating table and end his war on Ukraine.
“Russia’s economic problems have not had much bearing on Putin’s war aims so far, and the Kremlin will want to resist being strong-armed into a deal by the US,” Capital Economics said. “But the economic costs for Putin for continuing the war are likely to ratchet up.”