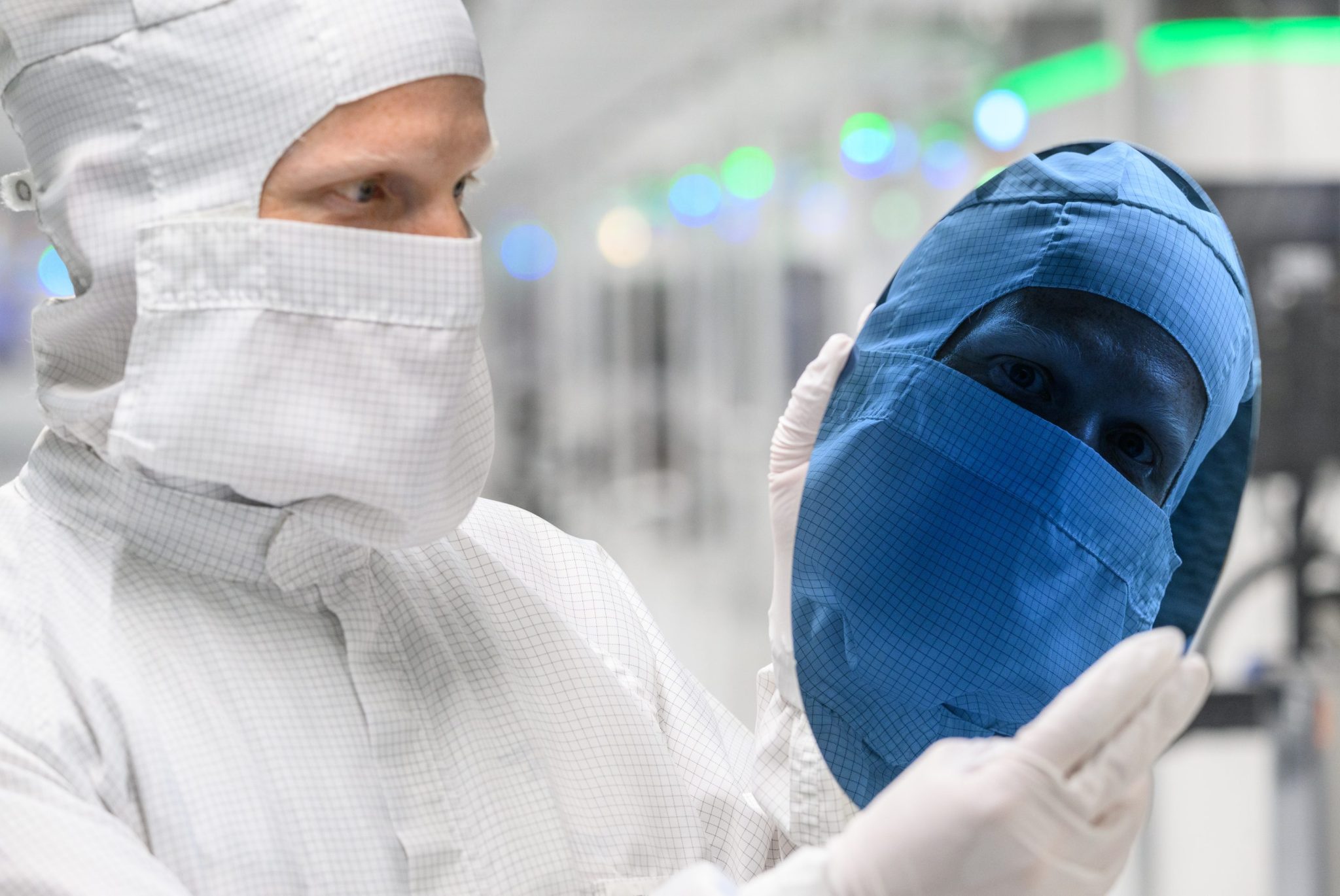
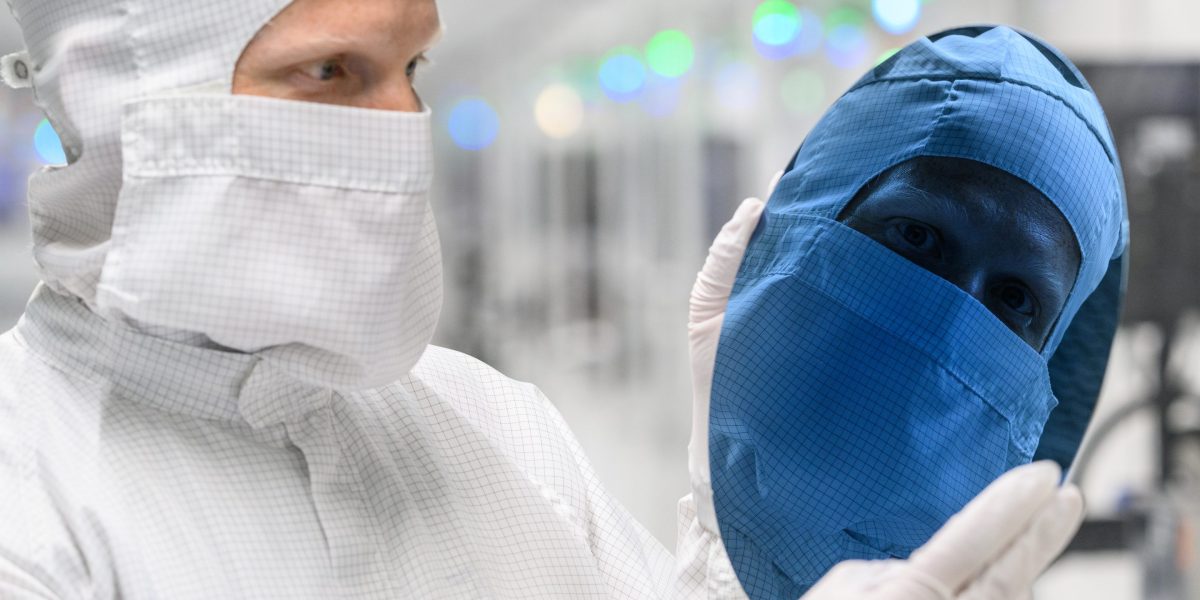
There’s renewed consideration on the sustainability of semiconductors. Refrain has been constructing in recent times to enhance the sustainability of chip manufacturing and utilization. In 2022, COP27 noticed the creation of a Semiconductor Climate Consortium with 60 founding members pledging to cut back emissions to 0% by 2050.
It’s comprehensible why chips could be a goal. They’re ubiquitous and their quantity and utilization will simply maintain rising. Most levels of their advanced provide chain–from the extraction of uncooked supplies to transportation of completed items to the processing, heating, and cooling required in manufacturing, to recycling–produce vital emissions.
Silicon, the essential materials used to construct chips, is famously created in furnaces from sand or quartz by burning a mix of coal and wooden chips. Power and water wants for the business to operate are excessive–and maintain rising. The manufacturing of superior 3nm chips might eat almost 8 billion kilowatt-hours annually. In some instances, the affect on communities has been seen. TSMC, the world’s largest chip producer, consumes 6% of Taiwan’s electricity and 10% of its water, leading to water shortages. And the industry’s contaminants in the Bay Area have rendered plenty of websites poisonous.
Regardless of this, governments and semiconductor corporations should be cautious about how they strategy chip sustainability presently. We simply went via a chip scarcity that introduced the economies to their knees. The scarcity additionally delivered to the fore the potential financial and nationwide safety advantages of accelerating and localizing chip manufacturing. The CHIPS and Science Act handed earlier this yr within the U.S. has generated momentum behind chip manufacturing–and sustainability points should be addressed in a manner that doesn’t sluggish this momentum.
This received’t have as a lot price as one might think about. Many of the present focus is on emissions–and the chip business produces solely 0.1 to 0.2% of world carbon dioxide equal emissions. That is small when contemplating the outsized financial affect they produce.
Chips function key enablers for sensible grids, the transition to renewables, clever and electrical transportation, low carbon footprint logistics and provide chains, video conferencing, sensible agriculture, drug discovery, and energy-efficient manufacturing, every serving to make progress towards international sustainability objectives. The financial affect of chips additionally helps higher adoption of sustainable applied sciences. One might argue that the end-to-end sustainability affect of chips is probably going constructive–regardless of their emissions and enormous vitality and water wants.
What does a cautious strategy to chip sustainability imply immediately?
A traditional regulatory strategy might result in a Nationwide Environmental Coverage Act (NEPA)-triggered environmental overview for every new chip manufacturing venture earlier than CHIPS Act funds may be disbursed. It could additionally permit litigation by personal residents at every step of the method. Nonetheless, this will introduce multi-year delays in a cost-conscious and fast-moving business. These delays (environmental evaluations take greater than 4 years, on common) and the corresponding improve in venture prices might defeat the important thing goal of the act–outpacing financial and geopolitical opponents and securing chip provides. As a substitute, one-time exceptions must be made that can permit fab constructions and upgrades to start out with little delay.
One might argue that this “free pass” might each be harmful and set a nasty precedent. Nonetheless, the chip business has completed effectively with purpose setting and self-regulation. TSMC now invests 2% of its annual income in inexperienced initiatives and recycles over 85% of the water it makes use of. Intel makes use of renewable vitality for over 80% of its operations and produces extra contemporary water than it consumes within the US, India, and Costa Rica. Samsung reuses over half of its water. Each the vitality and water depth of chip manufacturing have been lowering quick. Using renewable vitality has been on the upswing. New gear and processes are significantly extra vitality environment friendly.
One key purpose why the chip business has completed a lot is that improved sustainability aligns with their financial targets. Decreasing vitality, gasoline, and water necessities reduces their prices and gives them flexibility when it comes to location. Chipmakers have sufficient margins to soak up short-term prices. And their clients typically require assembly sustainability targets.
Along with one-time NEPA exceptions, regulators must be versatile when contemplating metrics on which the business has not completed effectively. Chip manufacturing processes have been developed and perfected over many years. Changing elements of the method with their extra sustainable counterparts would require giant investments into analysis and improvement with no ensures of success.
Equally, immediately’s semiconductor provide chains are extraordinarily optimized for effectivity and value. A careless relocation of provide chain elements merely to fulfill sustainability metrics can affect price and competitiveness. Particular flexibility must be proven with brownfield chip manufacturing. The price of retrofitting older fabs (or changing their instruments, services, and processes) that principally produce low-margin chips might render these fabs uncompetitive. Chip safety issues are inflicting a restructuring of current provide chains. Care should be taken that the compliance burden doesn’t produce unreliable or uncompetitive provide chains.
The chip business should develop–financial and nationwide safety calls for it. It is usually obligatory for this development to be sustainable. Because the business is at an inflection level, will probably be essential to be versatile and pragmatic.
Rakesh Kumar is a professor within the Electrical and Pc Engineering division on the College of Illinois and the writer of Reluctant Technophiles: India’s Sophisticated Relationship with Know-how.
Extra must-read commentary printed by Fortune:
- Financial pessimists’ wager on a 2023 recession failed. Why are they doubling down in 2024?
- COVID-19 v. Flu: A ‘much more serious threat,’ new research into long-term dangers concludes
- ‘Parroting Putin’s propaganda’: The enterprise exodus over Ukraine was no Russian bonanza
- The U.S.-led digital commerce world order is under attack–by the U.S.
The opinions expressed in Fortune.com commentary items are solely the views of their authors and don’t essentially replicate the opinions and beliefs of Fortune.