Final 12 months’s best-performing asset class wasn’t tech shares or derivatives: it was so-called “catastrophe bonds,” a little-known class of economic devices that shield in opposition to losses from pure disasters.
After years of gradual development, consultants say a breakout 2023 will push the $40 billion cat bond market nearer to its “Holy Grail” of lastly reaching the mainstream. Large returns helped by fortunate climate patterns yielded roughly 20% returns for cat daring holders, who like them as a hedge as a result of their efficiency has little correlation with broader monetary markets. New cash is predicted to pour on this 12 months as buyers chase these large yields—however whereas that’s good for the general market, it might backfire on the uninitiated.
“It does offer a real diversification tool,” Florida State College insurance coverage professor Charles Nyce instructed Fortune. “If my shares of Google go down or my shares of Apple go down because of an economic downturn, that shouldn’t have a big effect on my cat bonds.”
And the robust state of the surroundings, to say the least, means cat bonds aren’t going wherever. As they work in symbiosis with the $120 billion climate-related insurance coverage market, each are poised to only continue to grow as pure disasters get stronger and extra frequent. A new AON report discovered, as an illustration, that local weather catastrophes induced $380 billion in financial losses final 12 months, and local weather scientists warn of a “new normal” in multibillion-dollar disasters of this kind. So what’s the issue for buyers looking for a hedge?
“2023 was an outstanding year, with almost a 20% return on some of the indices,” says Nyce, who additionally holds grasp’s and doctoral levels in insurance coverage and threat administration from the College of Pennsylvania’s Wharton Faculty, however “[That was] well above what we’ve seen in the past. I don’t expect that to repeat itself.”
An all-time 12 months
One other disaster insurance coverage knowledgeable, Steve Evans, founding father of business publication Artemis, who’s been overlaying cat bonds for over 20 years, says that this distinctive asset class began coming of age earlier than the brand new millennium.
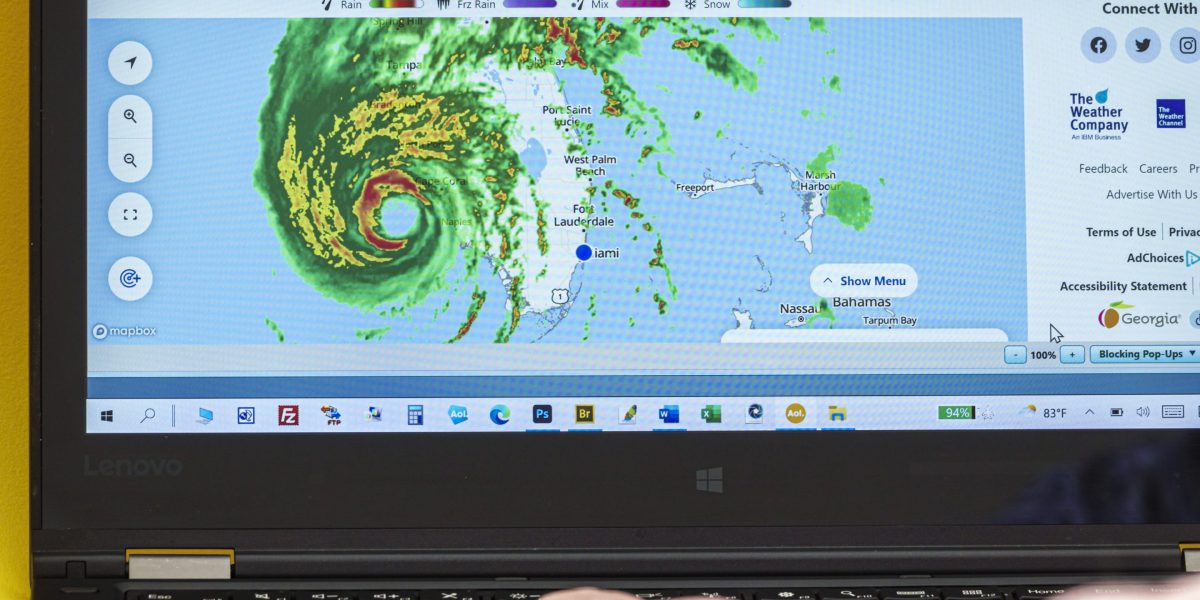
“It became very clear around the mid-’90s that if you had the Miami category five hurricane, or if you had the San Francisco or Los Angeles earthquake … the insurance industry was going to actually struggle to have the capital to absorb a loss of that size,” Evans stated. For insurance coverage firms overlaying these occasions, claims for a single huge storm might threaten to wipe out all of their capital.
That’s the place the reinsurance market is available in. For years, specialised suppliers have provided insurance policies that present insurance coverage for different insurance coverage firms. However as local weather dangers proceed to develop, conventional insurance policies simply aren’t providing sufficient protection. That’s why cat bonds have emerged in its place type of insurance coverage the place a bigger pool of buyers, not only a few reinsurance firms, can take up among the threat.
“A $50 billion loss can be catastrophic to an insurer,” explains Nyce. “The difference is, when you think about capital markets, a $50 swing … is something they could lose in a day and make up the next day. The Holy Grail has always been, ‘let’s get to the capital markets, where the magnitude of these losses is not as significant.’”
How cat bonds work
Insurance coverage firms can problem cat bonds, which promise an everyday coupon and full compensation at a specified date similar to another bond, to anybody who will purchase them. However the distinction is {that a} pure catastrophe which causes large insurance coverage losses can “trigger” the cat bond and let the issuing insurance coverage firm declare its full worth to cowl itself. That elevated threat means yields will be excessive—nearly 20% last year.
These juicy yields have made cat bonds a main goal for a number of area of interest hedge funds. Connecticut-based Fermat Capital Administration simply had its best year ever with a cat bond-heavy technique that yielded roughly 20% returns.
Cat bond buyers’ stability sheets benefited in 2023 from robust market circumstances and a wholesome quantity of fine luck. For one, Hurricane Ian, which caused nearly $13 billion in insurance losses after it hit Florida in 2022, scared the market and pushed charges up. These excessive yields had been solely elevated by rising development prices that made it extra expensive to rebuild after a pure disaster. And though main disasters did strike in 2023—earthquakes in Turkey and Syria and wildfires on Maui, for instance—they didn’t set off vital losses within the cat bond market, so buyers had been in a position to money of their bets with barely any losses.
Uncorrelated dangers, uncorrelated returns
One of many key attracts of investing in cat bonds is that climate occasions have little correlation with monetary markets, which suggests buyers should buy up cat bonds to be much less susceptible to general financial swings.
That diversification potential and final 12 months’s document returns are drawing increasingly buyers into the cat bond market—Evans says he’s already seeing the distinction. However a flood of latest capital doesn’t assist all people.
On one hand, extra money flowing into bond issuers’ pockets means broader protection and better entry to the huge capital markets they’ve been making an attempt to get to for years.
“I think the big thing for cat bonds is piercing $50 billion [in market capitalization],” stated Nyce. “These need to be scaled up more … [big returns] are the kind of stuff that will draw interest from investors.”
Ready for The Large One
Of the roughly 280 cat bonds presently tradeable, roughly half have publicity to essentially the most harmful pure catastrophe on any insurer’s thoughts—a class 5 hurricane hitting Miami. However because the market grows and local weather disasters develop into extra widespread elsewhere, insurers are issuing bonds that target extra area of interest, regional occasions, too. That’s a key supply of the cat bond business’s development.
“Between 40% and 60% of the market is exposed to a major, category five US hurricane,” stated Evans. “The market began very much focused on [those] ‘peak perils,’ and has then expanded out a little bit more to include other types of perils as well. We’ve seen everything from wildfire to meteorite impact risk transferred now.”
However there may very well be a value to a flood of buyers shopping for up cat bonds in quest of excessive yields—when it comes to diminishing worth and ground-floor patrons dropping their edge.
“If you flood the market with capital … that typically results in more competition and typically pressures pricing a bit. I think there’s a bit of a desire to just be a bit more cautious about capital raising and how much actually comes in over the next year,” stated Evans.