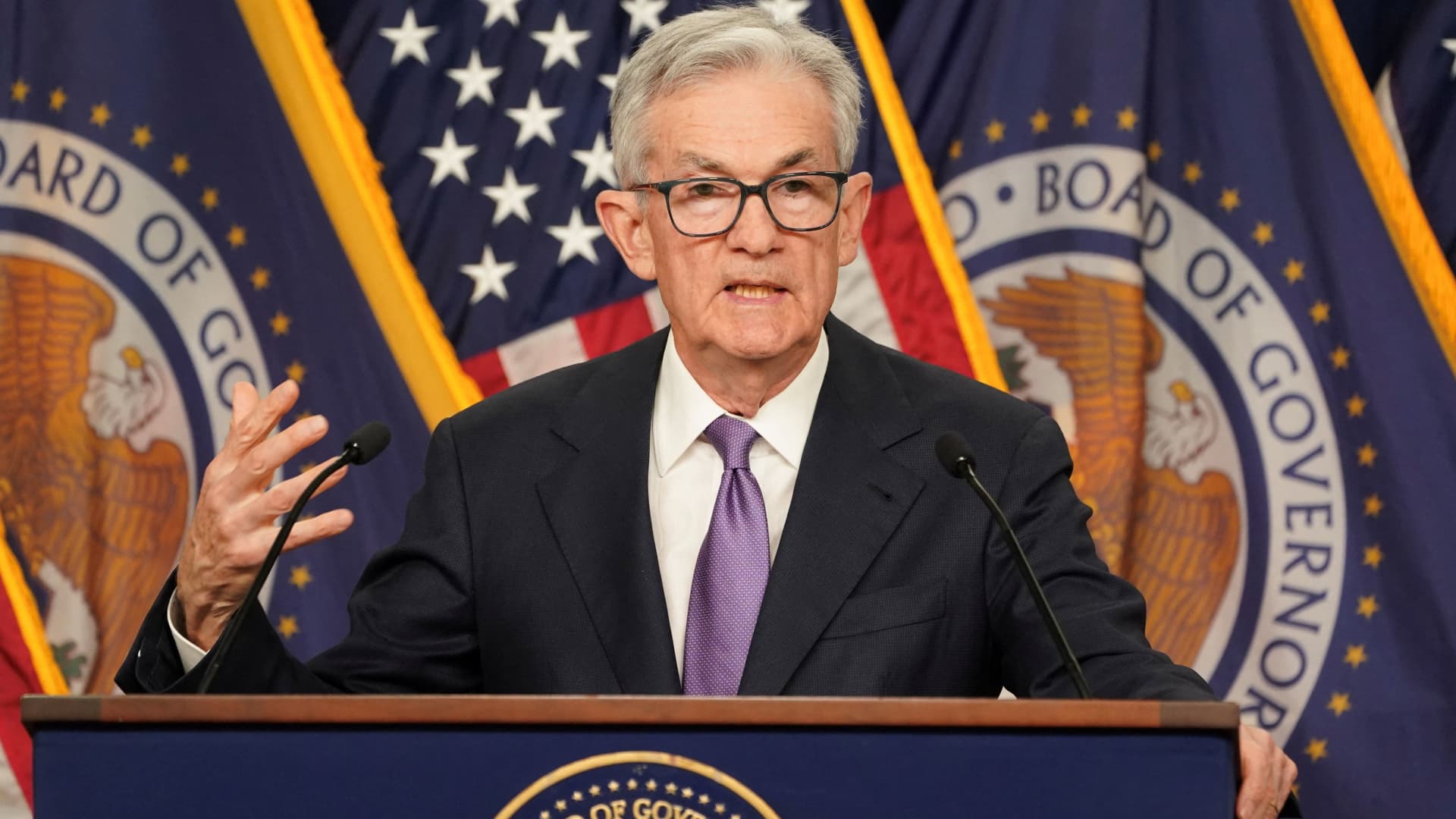
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell speaks throughout a press convention following a closed two-day assembly of the Federal Open Market Committee on rate of interest coverage on the Federal Reserve in Washington, D.C., on Dec. 13, 2023.
Kevin Lamarque | Reuters
Fed Chair Jerome Powell mentioned Wednesday that the distinctive financial circumstances created by the Covid-19 pandemic have helped the central financial institution’s effort to convey down inflation with out inflicting a recession, a uncommon feat in financial historical past.
The Federal Reserve signaled in its newest economic projections that it’s going to minimize rates of interest in 2024 even with the economic system nonetheless rising, which might probably be a path to the “soft landing” that many economists seen skeptically when the central financial institution started aggressively climbing charges final 12 months to battle post-pandemic inflation.
“This inflation was not the classic demand overload, pot-boiling over kind of inflation that we think about. It was a combination of very strong demand, without question, and unusual supply-side restrictions, both on the goods side but also on the labor side, because we had a [labor force] participation shock,” Powell mentioned at a press convention after the Fed’s final assembly of the 12 months.
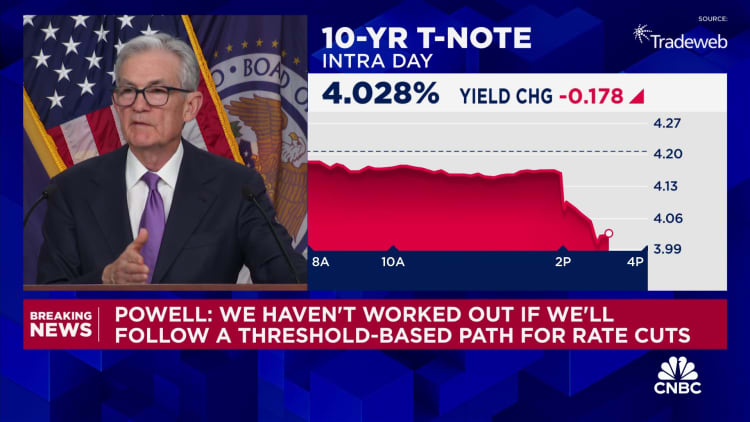

The Fed has seen its inflation battle as a two-front battle of making an attempt to weaken the demand within the economic system whereas the “vertical” provide curve normalized, Powell mentioned. The availability aspect of assorted components of the economic system is now getting nearer to the place it was pre-pandemic, he mentioned.
“Something like that has happened, happened so far. The question is once that part of it runs out — and we think it has a ways to run… — at some point, you will run out of supply side help and then it gets down to demand, and it gets harder. That’s very possible, but to say with certainty that the last mile is going to be different, I’d be reluctant to say we have any certainty around that,” Powell mentioned.
“So far, so good, although we kind of assume it will get harder from here,” he added.
The outline of the economic system is much like how Powell and different Fed members described the inflation scenario in 2021, generally saying that the speedy worth will increase would show to be “transitory.” The central bankers dropped that language as inflation accelerated after which started aggressively climbing charges in March 2022. The Fed has hiked its benchmark fee greater than 5 proportion factors in complete since then.
Powell has maintained over the previous 12 months and a half that it was nonetheless doable, although not essentially doubtless, that the U.S. economic system might obtain a “soft landing,” the place inflation returned to the Fed’s 2% goal with out inflicting a big rise in unemployment.
Although fee hikes to sluggish inflation are sometimes related to recessions, the U.S. economic system has generally expanded throughout such cycles earlier than, most notably within the mid-Nineties.
Whereas many economists and Wall Avenue forecasters entered the 12 months projecting a recession in 2023, the U.S. economic system has as a substitute confirmed surprisingly resilient. The inventory market has additionally rallied after a deep sell-off in 2022, with the Dow Jones Industrial Common closing at a record high on Wednesday.
Though Powell mentioned the U.S. economic system has “slowed substantially” in latest months, the Fed nonetheless initiatives GDP to develop 1.4% subsequent 12 months.
Do not miss these tales from CNBC PRO: