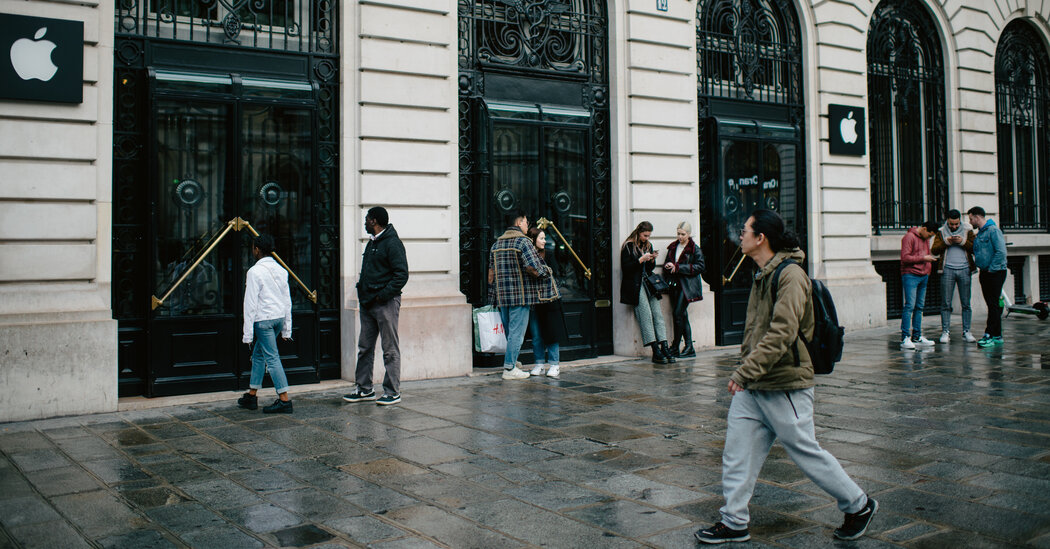
Since Apple launched the App Store in 2008, it has tightly managed the apps and companies allowed on iPhones and iPads, giving the corporate an iron grip on one of many digital economic system’s Most worthy storefronts.
Now Apple is weakening its maintain on the shop, in probably the most consequential indicators so far of how new European regulations are altering shopper know-how.
To adjust to a European Union competitors legislation taking impact on March 7, Apple on Thursday introduced main adjustments to the App Retailer and different companies for shoppers in Europe. Customers of iPhones and iPads within the 27-nation bloc will for the primary time be capable of use different app shops to obtain video games, productiveness instruments and different apps. Banks and procuring companies can provide competing cost strategies inside their apps. Individuals who purchase new iPhones sooner or later will even see a brand new menu for downloading different browsers to Apple’s Safari, equivalent to Chrome and Firefox.
The adjustments are a few of the most tangible examples of how a checkerboard of laws and regulations is now fracturing folks’s know-how experiences based mostly on the place they stay. In China, authorities guidelines drive Apple to dam apps like virtual-private networks, often known as VPNs, which might give customers entry to the unfiltered web. In Europe, prospects will now have entry to competing app shops and different companies. In america, the place there are fewer legal guidelines and laws, Apple and different tech giants have extra flexibility to function as they please.
The shifts within the App Retailer stem from a 2022 legislation handed by the E.U. referred to as the Digital Markets Act. The far-reaching legislation was aimed toward loosening the facility of the world’s largest tech corporations in areas like e-commerce, social media and messaging. Amazon, Meta, Google and Microsoft have additionally introduced adjustments to adjust to the brand new guidelines.
“The changes we’re announcing today comply with the Digital Markets Act’s requirements in the European Union, while helping to protect E.U. users from the unavoidable increased privacy and security threats this regulation brings,” Phil Schiller, who leads the App Retailer, stated in a press release.
Europe accounts for about 6 % of Apple’s whole App Retailer gross sales, that are estimated to be $24 billion yearly worldwide.
E.U. regulators have lengthy raised alarms that Apple abuses its management over the App Retailer to stifle competitors. The Silicon Valley firm has argued that its gatekeeper position protects prospects from malware, privateness breaches and flawed apps. However app builders like Spotify and Epic Games, the maker of Fortnite, have stated Apple misuses its energy by demanding they pay excessive charges and forcing them to make use of underlying know-how that it makes.
For years, Apple has resisted making the sorts of adjustments it introduced on Thursday. It’s unclear if the strikes will fulfill European regulators who’ve vowed to aggressively implement compliance with the Digital Markets Act.
Apple stated it will preserve some oversight of latest marketplaces and apps working outdoors its App Retailer, however warned that the brand new E.U. insurance policies would give dangerous actors a brand new path to distribute malware and defraud prospects. The corporate stated that it created a system to watch all iOS apps, approve different app shops and monitor different cost programs.
Apple stated builders would even be charged a price of fifty euro cents for each obtain of their app after it has been downloaded 1 million occasions or extra inside a 12-month interval, no matter whether or not it was by way of the App Retailer or another. This will even apply to free apps, however not apps distributed by authorities, schooling and nonprofits.
The brand new guidelines may dent Apple’s funds. The App Retailer’s coverage of taking as much as 30 % of builders’ gross sales has made it a crucial piece of the corporate’s practically $400 billion enterprise. Nevertheless it has additionally opened Apple to criticism and regulatory scrutiny as a result of many builders complained that the charges have been unjust.
In Europe, Apple stated that builders utilizing the App Retailer would have the choice to proceed utilizing the prevailing fee phrases, or transfer to a brand new price construction. This would come with a lowered fee price of as much as 17 % for digital items and companies. A further price of three % can be charged to builders who use Apple’s cost system.
Apple stated its charges are to cowl the prices of creating its software program and offering instruments to builders.
Builders who distribute their app by way of a competing App Retailer wouldn’t be topic to any Apple fee. Builders who present hyperlinks to finish funds outdoors their apps may forgo the charges.
Builders would additionally be capable of keep away from what a few of them have stated is a cumbersome evaluate course of by Apple of the apps it distributes in its retailer. However the firm has created a brand new system, which it calls notarization, to keep up some management over the apps distributed throughout iPhones. Each iPhone app will embrace an set up key to offer Apple with data on when it was put in and permit the corporate to do automated scans for malware.
As a part of the notarization course of, apps will present Apple with descriptions and screenshots of the companies they provide, in addition to the identify of the builders. Apple will share that data with iPhone customers earlier than an app is downloaded.
Apple additionally launched a brand new function for purchasers to make use of alternate options to its Pockets app for cellular funds, an more and more frequent type of cost for public transportation, eating places and cafes. Main banks and companies like PayPal can now provide competing companies.
Apple has challenged some parts of the brand new European legislation, together with a requirement that may open its messaging service, iMessage, to work extra easily with Android units. The corporate has argued that iMessage isn’t topic to the necessities as a result of it’s free to prospects.
The E.U. has not made a ultimate choice on the messaging challenge.