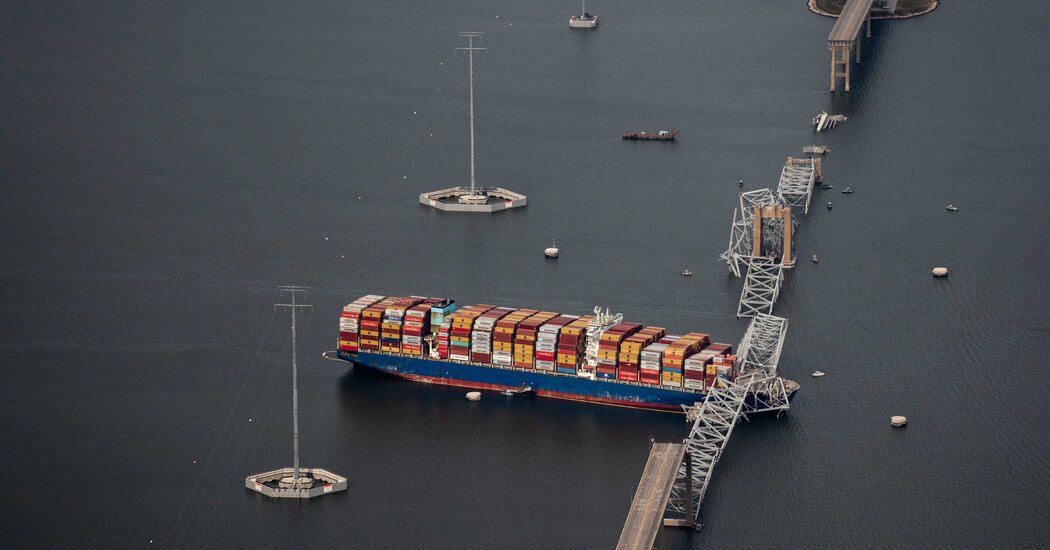
Simply minutes earlier than the cargo ship Dali was set to glide underneath Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge, the ship’s alarms started to blare. The lights went out. The engine halted. Even the rudder, which the crew makes use of to maneuver the vessel, was frozen.
As a frantic effort to revive the ship was underway, the pilot quickly acknowledged that the aimless vessel was drifting towards catastrophe, and known as for assist.
The cascading collapse of the vessel’s most important working techniques left the Dali adrift till it finally collided with the Key bridge, knocking the span into the river and killing six folks. However as crews this week had been nonetheless checking out how you can disentangle the ship and get better the our bodies of those that died, investigators had been additionally turning to essentially the most central query: What may have brought on such a catastrophic failure on the worst doable second?
Engineers, captains and transport officers around the globe are ready for that reply in an period when the trade’s largest ships can carry four times as much cargo as these just some a long time in the past, navigating via congested city ports underneath bridges that will carry tens of hundreds of individuals a day,
Already, a couple of key questions are rising, in line with engineers and transport consultants monitoring the investigation, and most of them level to {the electrical} turbines that energy practically each system on the 984-foot vessel, not solely the lights, navigation and steering, however the pumps that present gas, oil and water to the huge diesel engine.
The “complete blackout” reported by the pilot is tough to elucidate in at this time’s transport world, wherein massive business vessels now function with a spread of automation, computerized monitoring, and built-in redundancies and backup techniques designed to avert simply such a calamity.
“In the last 30 to 40 years, the level of that redundancy has been increasing quite considerably,” stated John Carlton, a professor of marine engineering at Metropolis, College of London. “The ship of today is so very different to the one of 30 years ago.”
But there’s a variety of doable components contributing to the failure that investigators must sift via as they interview crew members, study gas provides and scrutinize the ship techniques that broke down that evening.
If there was defective upkeep, it may have brought on a delay in beginning the emergency backup generator, or {an electrical} fault may have prevented it from remaining engaged. Contaminated gas or an inadvertently closed valve may have fouled or starved the primary turbines. Human error may have set off issues or failed to beat them. The ship’s personal automation may have led to gear glitches. Or a hearth may have damaged out and broken essential gear.
The solutions may have implications not just for worldwide transport but additionally for who’s chargeable for damages that S&P International Scores estimated at greater than $2 billion.
Grace Ocean Personal, the Singapore-based firm that owns the Dali, stated it was “fully cooperating with federal and state government agencies.” Grace Ocean’s proprietor is Yoshimasa Abe, a Japanese citizen who owns at the very least two transport traces and greater than 50 vessels, together with among the world’s largest container ships. Whereas the Dali was insured, Mr. Abe’s firm probably faces massive claims towards it, relying on the findings of the accident investigators.
Given the scope of the failure, it’s doable that there have been a number of issues. Timothy McCoy, a professor specializing in marine engineering on the College of Michigan, stated that very like a airplane crash, an in depth breakdown of a ship’s techniques sometimes contain a sequence of occasions.
A detailed have a look at the potential components entails most of the most important parts within the operation of a contemporary cargo vessel — together with the gas that feeds the ship’s 55,000-horsepower diesel engine that in flip powers the ship’s propeller.
Gas additionally powers the massive turbines that present electrical energy to container ships. And a ship just like the Dali wants electrical energy to run its primary engine — its gas injectors are electrically powered, for example — and steer its rudder. With out electrical energy, the ship can go adrift.
An outbreak of contaminated gas led to reported issues with 32 vessels from Texas to Singapore final August, maritime industry officials reported, with a few of them reporting lack of energy and propulsion at sea.
In Washington State final yr, a big passenger ferry ran aground after shedding energy because of bacterial and fungal development within the vessel’s gas tanks that fouled the ship’s filtration techniques.
On the time it was constructed, 2015, the Dali had 4 turbines, in line with S&P Maritime Portal, a transport information service. Not all of them run without delay, often, however container vessels leaving port will sometimes have an additional generator working, to supply reserve energy if wanted. “At least two should be online at the same time,” stated Mark Bulaclac, a tutorial on maritime points who has additionally served as an engineer on container ships.
If all turbines had been working on a typical supply of dangerous gas, that may have brought on all of them to fail.
Henry Lipian, a forensic crash investigator who beforehand labored within the Coast Guard, stated the sudden lack of the ship’s turbines led him to consider gas issues as a possible offender.
He stated investigators would wish to have a look at the gas on board, the way it was delivered, whether or not it had been examined beforehand and what filtration techniques had been on the ship. However he stated that an issue with the gas valves might be one other rationalization.
“I’d want to start tracing all of those fuel lines,” he stated.
In Baltimore, investigators had been within the strategy of accumulating a gas pattern from the Dali so as to study the standard, viscosity and indicators of any contaminants, stated Jennifer Homendy, the chair of the Nationwide Transportation Security Board.
But different consultants stated there have been additionally causes to doubt the contaminated gas situation. New fuels sometimes endure testing, and duplicate filtration techniques might help clear out problematic parts that weren’t flagged in testing. No studies have emerged of different ships having an issue from the identical batch of gas.
Maritime engineers say {an electrical} chain response may even have brought on all of the turbines to go down. When one generator fails, it will possibly create a scenario in which there’s an excessive amount of demand for too little provide of electrical energy. Different turbines are then vulnerable to being broken, so the system will shut them down, too, stated Richard Burke, a professor of naval structure and marine engineering at SUNY Maritime Faculty in New York.
“It’s as if you and I are both holding up a heavy weight and I let go,” he stated, “You can’t hold it by yourself, so you drop the weight.”
A haywire generator may additionally zap {the electrical} distribution system on the ship, stated Capt. Morgan McManus, an teacher at SUNY Maritime Faculty.
When all the primary turbines fail, ships depend on a backup generator that’s sometimes located above the water line in one other space of the ship, with its personal gas supply.
Marine engineers say backup turbines present electrical energy to run some lights, the navigation system — and, crucially, the ship’s steering system. With out at the very least backup energy, the rudder can’t be moved.
As a result of some lights got here again on after the Dali skilled its preliminary blackout, it seems the backup generator did activate, however solely after a roughly one-minute delay. Even then, the lights appeared to return off, then on once more, elevating the potential for an issue with the backup generator.
Ms. Homendy of the N.T.S.B. stated this week that investigators had collected information “consistent with a power outage” however had been nonetheless attempting to find out the extent.
Clay Diamond, the pinnacle of the American Pilots’ Affiliation, a commerce group that has been in shut contact with the harbor pilots in Maryland, stated that steering was restored after the emergency generator got here on-line. However even with a tough flip to the left and the dropping of an anchor, there was not sufficient time to show or cease the ship.
Mr. Bulaclac, the transport engineer, stated backup turbines are supposed to be commonly examined by turning them on for 2 hours as soon as a month. “What I would like to know is when that emergency diesel generator was last tested,” he stated.
The Coast Guard inspected the Dali when it docked within the Port of New York in September however discovered no deficiencies on the ship. The Coast Guard didn’t present particulars of what it inspected.
The modernization of ships might have launched different methods vessels can fail. They’ve more and more trusted computer systems to watch for troubles and take motion when an issue is recognized. In some methods, this can be a built-in layer of computerized safety: If one element will get overloaded, it may be mechanically shut down to stop additional harm. However these shutdowns could cause issues on their very own.
“I could not rule out that some computer failure shut all the valves off or shut off pumps that provide the fuel,” Mr. Lipian stated.
Michael Forsythe and Jenny Gross contributed reporting.