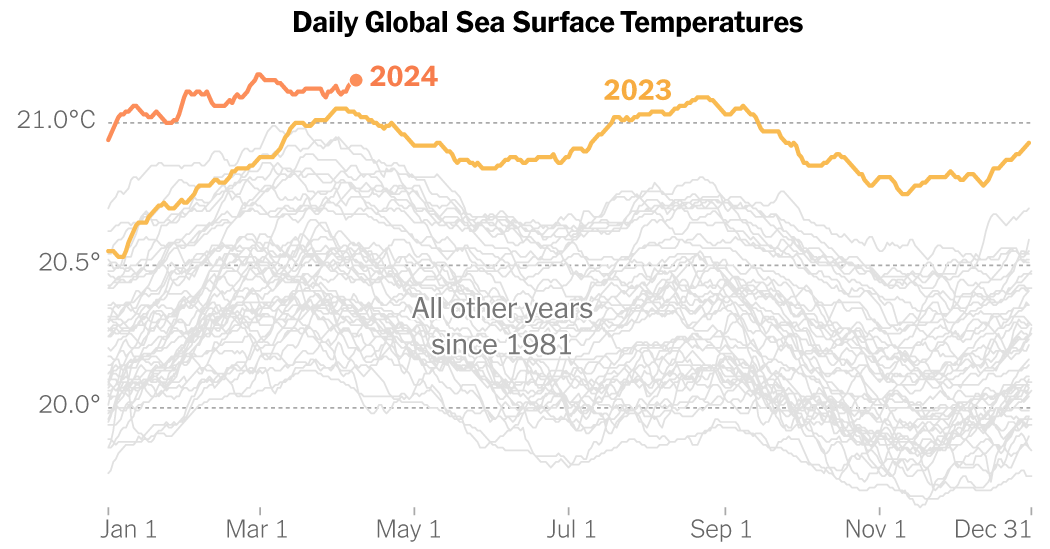
The ocean has now damaged temperature information day by day for greater than a yr. And to this point, 2024 has continued 2023’s pattern of beating earlier information by large margins. The truth is, the entire planet has been scorching for months, in accordance with many alternative knowledge units.
“There’s no ambiguity about the data,” mentioned Gavin Schmidt, a climatologist and the director of the NASA Goddard Institute for Area Research. “So really, it’s a question of attribution.”
Understanding what particular bodily processes are behind these temperature information will assist scientists enhance their local weather fashions and higher predict temperatures sooner or later.
Final month, the common international sea floor temperature reached a new monthly high of 21.07 degrees Celsius, or 69.93 levels Fahrenheit, in accordance with the Copernicus Local weather Change Service, a analysis establishment funded by the European Union.
“March 2024 continues the sequence of climate records toppling for both air temperature and ocean surface temperatures,” Samantha Burgess, deputy director of Copernicus, mentioned in an announcement this week.
The tropical Atlantic is abnormally heat, serving to set the stage for a busy hurricane season, according to an early forecast by scientists at Colorado State College. Increased ocean temperatures present extra power to gas stronger storms.
International temperatures are rising long-term as a result of the burning of fossil fuels provides greenhouse gases, which heat the planet, to the ambiance. Up to now, local weather change has raised the worldwide common temperature by about 1.2 levels Celsius, or 2.2 levels Fahrenheit, above the preindustrial common temperature. And since it takes extra power to warmth up water than air, the oceans have absorbed the vast majority of the planet’s warming from greenhouse gases.
However the “massive, massive records” set over the previous yr are past what scientists would anticipate to see even contemplating local weather change, Dr. Schmidt mentioned.
What’s totally different now, in contrast with this time final yr, is that the planet is coping with the consequences of an El Niño occasion that started in July. El Niño occasions are pure local weather patterns related to elevated temperatures.
“The temperatures that we’re seeing now, the records being broken in February and March, are actually much more in line with what we would expect,” in contrast with these of final yr, Dr. Schmidt mentioned. “Let’s see what happens by the summer.”
El Niño is weakening and anticipated to dissipate quickly. What occurs to international common temperatures then would assist make clear the temperatures of 2023, he mentioned.
Along with local weather change and El Niño, there are a few different components that could be contributing to those dizzying information.
One is a current discount in aerosol air pollution from container ships traversing the ocean, following new worldwide gas requirements that took impact in 2020. Satirically, aerosols have a cooling effect within the ambiance, and had been serving to to masks the true extent of local weather change till now.
There was additionally the massive eruption of the underwater Hunga Tonga-Hunga Haʻapai volcano in 2022. Volcanic eruptions that occur on land ship up plumes of soot and aerosols, which block daylight and quickly cool the ambiance. However as a result of this volcano was submerged underneath the Pacific Ocean, its eruption additionally sprayed thousands and thousands of tons of water vapor into the higher ambiance. Water vapor is a robust greenhouse gasoline.
“It was the most explosive eruption since Krakatau, and usually the year after is when you see the impacts,” mentioned Sean Birkel, an assistant professor on the College of Maine Local weather Change Institute, who created a local weather knowledge visualization software known as Local weather Reanalyzer. He suspects the warming impact of the volcanic eruption has been bigger than early estimates advised, noting that the eruption could have affected atmospheric circulation and helped amplify the El Niño that developed in 2023. However, he added, extra analysis is required.
Dr. Schmidt identified that when scientists put collectively their estimates to this point of how a lot the volcanic eruption, the diminished transport air pollution, El Niño and local weather change ought to heat the planet, the numbers don’t add up.
“There could be still something missing,” he mentioned, like different sources of aerosol air pollution having improved greater than researchers know, or Earth’s local weather having extra inside variability than anticipated, or international warming amplifying the consequences of El Niño.
A number of teams of scientists are working to get a clearer image, Dr. Schmidt mentioned, and he expects outcomes to start out being printed within the subsequent few months.
Nadja Popovich contributed reporting.