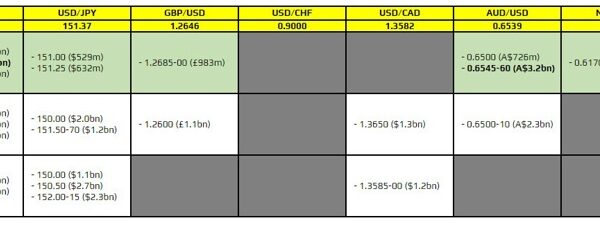
If what goes up should come down, then the pressing query on the minds of many in Europe is when will rates of interest start dropping? For months, charges have been set on the highest within the European Central Financial institution’s historical past.
Traders have been betting that the central financial institution will minimize charges fairly quickly — presumably in April. Merchants determine charges should come down as a result of inflation has slowed notably — it’s been beneath 3 % since October — and the area’s financial system is weak. By the top of 12 months, the central financial institution can have minimize charges by greater than 1 share level, or between 5 and 6 quarter-point cuts, buying and selling in monetary markets implied.
Policymakers, nevertheless, try to drag market opinion within the different course and delay the expectations of price cuts. Most of the central financial institution’s Governing Council are cautious of declaring victory over inflation too quickly, lest it settle above the financial institution’s goal of two %.
On Thursday, the European Central Financial institution caught to this outlook. It held rates of interest regular, leaving the deposit price at 4 %, the place it has been since September.
Charges are at ranges that, “maintained for a sufficiently long duration, will make a substantial contribution” towards returning inflation to 2 % in a “timely manner,” Christine Lagarde, the president of the financial institution, stated on Thursday.
The area must be “further along” within the disinflation course of earlier than the financial institution will be assured that inflation will keep at goal, she added.
Not now, however in all probability in the summertime
There was a shift on the central financial institution just lately. In December, Ms. Lagarde stated rate cuts hadn’t been discussed and emphasised the must be vigilant in opposition to inflation. However the brand new 12 months introduced a slight change of tune. And final week, Ms. Lagarde stated in an interview with Bloomberg Information that it was likely that rates could come down in the summer.
Requested about this once more at a information convention in Frankfurt on Thursday, Ms. Lagarde stated the 26-member Governing Council nonetheless agreed that it was “premature to discuss rate cuts.” Policymakers would make their selections primarily based on incoming financial information, not by following a calendar, she stated, seemingly in an effort to maintain bets on price cuts at bay.
Nonetheless, she stated, “I typically stand by my comments.”
It’s a remark merchants have seized on, and they’re now firmly anticipating a price minimize on the financial institution’s June assembly, whereas bets for April have elevated.
Central banks have to decide on their phrases fastidiously to information markets as a result of it issues what buyers suppose. If merchants start to anticipate decrease rates of interest, they will transfer the markets in that course and ease monetary situations earlier than the central financial institution would really like. That might probably undermine efforts to restrain the financial system and gradual inflation. This began to occur in earnest late final 12 months, after the Federal Reserve signaled it will minimize charges this 12 months, which caused markets to move in the USA and internationally.
Delaying expectations
Policymakers have tried to delay expectations of price cuts till a minimum of the summer season, arguing they gained’t have the info they want, notably on wage development, till their assembly in June.
“The E.C.B. will err on the side of caution,” stated Oliver Rakau, chief German economist at Oxford Economics, as a result of they’re nervous about being fallacious once more on inflation, after beforehand underestimating its energy.
In the meantime, those that say inflation will hold slowing are counting on the financial system not enduring any extra main shocks. Assaults on industrial ships within the Purple Sea has prompted shipping prices to spike and analysts are warning that it might result in a resurgence in inflation if the disruption goes on for a very long time and people price will increase are handed to customers.
Sooner fairly than later?
Then again, information reveals inflation has been easing sooner than the central financial institution predicted. Headline inflation ticked up in December as some authorities help measures ended, however might fall beneath 2 % by the autumn, based on economists at Berenberg financial institution.
The area’s financial system can also be weak, not overheating. Germany, the most important financial system within the bloc, is sluggish, after information confirmed it contracted 0.3 percent last year. Separate information printed this week confirmed that demand for loans from companies and households throughout the eurozone was persevering with to say no.
However its doable to have a look at this case considerably positively, based on Frederik Ducrozet, head of macroeconomic analysis at Pictet Wealth Administration. “It could have been much, much worse,” he stated. For instance, the recession in Germany might have been considerably deeper, he added. “Inflation was a disaster,” he stated. “It’s not under control but is going in the right direction.”
He expects the central financial institution to start out reducing charges in June and minimize them by a full share level in mixture by the top of the 12 months. Different economists, together with these at Goldman Sachs and Deutsche Financial institution, predict price cuts to start in April.
Whereas there’s a debate over how quickly and how briskly charges will go down, most economists agree that the ultralow charges are a factor of the previous.
“The very low charges we had seen prepandemic are unlikely to return, stated Mr. Rakau of Oxford Economics, as a result of there’s a a lot larger must borrow cash to speculate, notably in renewable vitality and new applied sciences.