The fast growth of artificial intelligence has led some to concern harmful situations the place the know-how is smarter than the people who created it, however some consultants imagine AI has already reached that time in sure methods.
“If you define it as performing intellectual but repetitive and bounded problems, they already are smarter. The best chess players and GO players are machines. And soon we can train them to do all tasks like that. Examples include legal analysis, simple writing and creating pictures on demand,” Phil Siegel, the founding father of the Heart for Superior Preparedness and Risk Response Simulation, informed Fox Information Digital.
Siegel’s feedback come after a new survey of practically 2,000 AI consultants discovered that opinions differed as to when the know-how would have the ability to outsmart people. To slim down simply how sensible AI might be, respondents got a listing of human duties starting from writing a highschool historical past essay to full automation of all human labor and tasked with predicting when AI could be as much as the duty.
IMF WARNS AI WILL IMPACT 60% OF US JOBS, INCREASE INEQUALITY WORLDWIDE

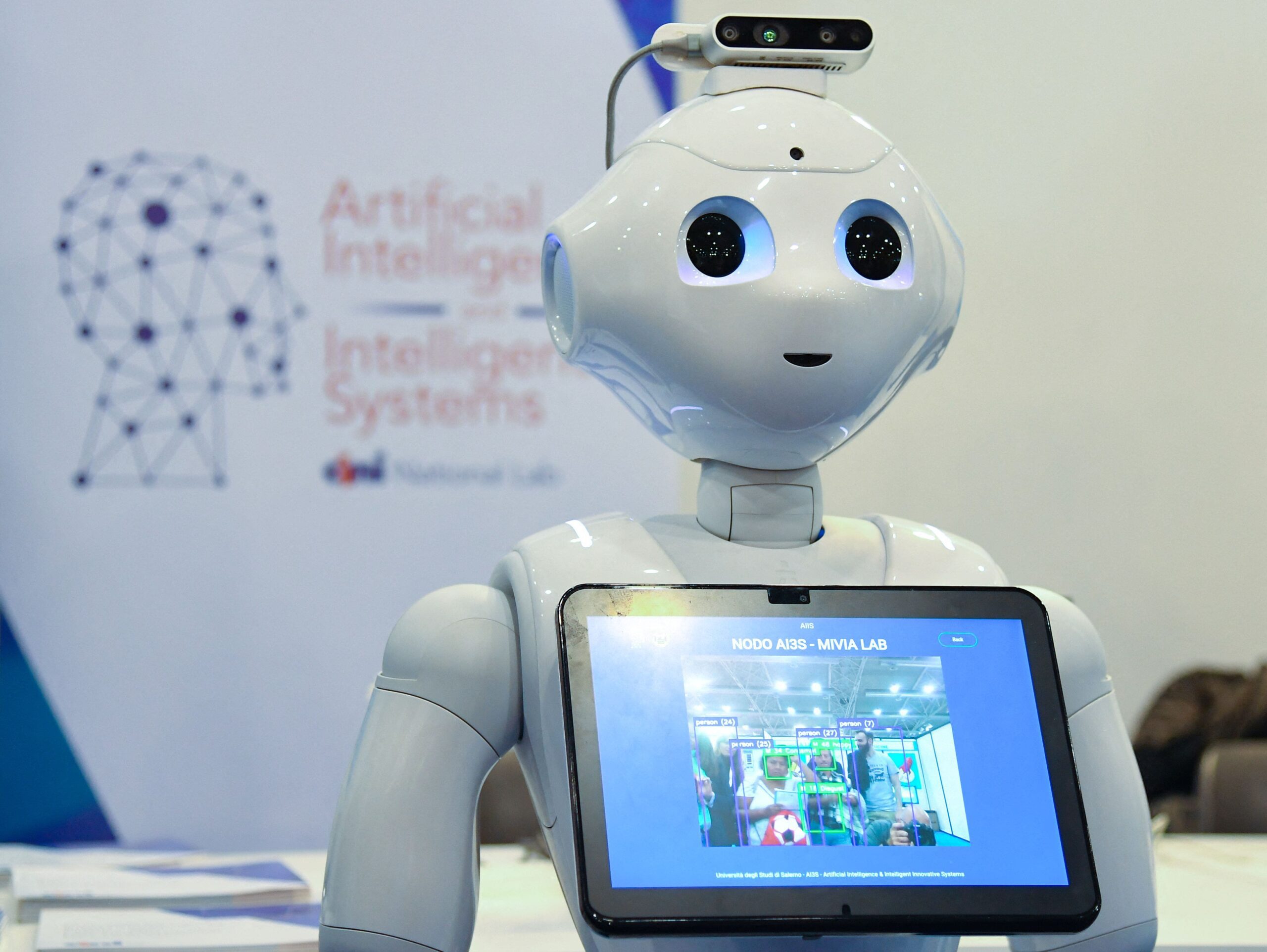
A robotic from the Synthetic Intelligence and Clever Methods laboratory of Italy’s Nationwide Interuniversity Consortium for Laptop Science is displayed on the seventh version of the Maker Faire. (Andreas Solaro/AFP by way of Getty Pictures)
For some duties such because the high school history paper, the consultants mentioned the know-how will already be able to the feat throughout the subsequent two years. However with the ability to substitute all human labor is extra distant, the survey discovered, with the vast majority of consultants predicting that such a feat won’t be achievable for AI this century.
“They can write short stories now, but they need lots more information about human nature to write a bestseller. They can write a movie, but maybe not a hit movie. They can write a scientific paper but can’t execute all the instructions to perform a complex atomic level experiment at a supercollider,” Siegel mentioned of present AI platforms.
“Maybe someday they can do those things as well, but we need lots of data to train them to do things like that well. Then there is maybe another level — training them to read human nature on the fly to do complex decision-making like running a company or a university. The level of training for humans is so complex and not well understood for those tasks that it could take a very, very long time and huge computation for them to be superior at those tasks.”
“It’s not a question of if AI will outsmart us but when. We simply cannot compete with the raw processing power.”
Samuel Mangold-Lenett, a employees editor at The Federalist, shares an analogous sentiment, noting that some AI platforms can already perform duties that will be unattainable for people.
“AI is a relatively young field and products like ChatGPT can already do complex tasks and solve problems in a matter of seconds that would take humans months of complex thought and lifetimes of practice. So, in some ways, it already has outsmarted us,” Mangold-Lenett informed Fox Information Digital. “Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is something else that needs to be considered. Theoretically, AGI can surpass all the intellectual capabilities of man and can perform every economically important task. It may be better to ask whether AI is capable of attaining sentience and what this means for humanity.”
Some consultants imagine a world during which AI can outsmart its human creators is inevitable, opening up debate about how such technology will change society.

Staff Tartan Rescues CHIMP (CMU Extremely Clever Cell Platform) robotic makes use of a hand-held energy software throughout the reducing job of the Protection Superior Analysis Tasks Company Robotics Problem on the Fairplex on June 6, 2015, in Pomona, California. (Chip Somodevilla/Getty Pictures)
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND US NUCLEAR WEAPONS DECISIONS: HOW BIG A ROLE?
“It’s not a question of if AI will outsmart us but when. We simply cannot compete with the raw processing power,” Jon Schweppe, the coverage director of the American Ideas Challenge, informed Fox Information Digital. “This is the appeal and the value [added] of AI — the ability for a computer to process data and produce output in a much more rapid and efficient way than if humans were doing the work. But this will obviously have incredible effects on society — some good and some bad — so it will be important for our lawmakers to guide the tech companies and help them to chart a responsible path forward.”
A few of these developments might be harmful, warned Pioneer Improvement Group chief analytics officer Christopher Alexander, particularly if the know-how falls into the fingers of much less accountable actors.
“Our growing obsession with hypothetical Skynet situations has been derailing the serious policy conversations we need to have now about developing and deploying Al responsibly.”
“U.S. autonomous weapons systems, by policy design, are not allowed to kill human beings without a human approving, but consider this very plausible scenario: A defense contractor develops an AI that can control autonomous vehicles. The project is canceled, and the AI is incredibly effective but has some flaws. The Chinese, who have already stolen trillions of dollars of U.S. intellectual property over the past decade, steal the AI. The Chinese use the flawed AI in an autonomous drone and it runs [amok], killing innocent people and damaging property for two hours,” Alexander informed Fox Information Digital. “This won’t end the world, but it is certainly possible.”
However Jake Denton, a analysis affiliate on the Heritage Basis’s Tech Coverage Heart, informed Fox Information Digital among the extra excessive predictions in regards to the risks of AI have been exaggerated.


Robots play soccer in an illustration of synthetic intelligence on the stand of the German Analysis Heart for Synthetic Intelligence. (Sean Gallup/Getty Pictures)
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
“At this stage, the fear of superintelligent Al bringing about some form of techno-dystopia feels misplaced. These sci-fi doomsday scenarios have become a major distraction from the real and pressing issues we face with Al policy today,” Denton mentioned. “Our growing obsession with hypothetical Skynet situations has been derailing the serious policy conversations we need to have now about developing and deploying Al responsibly.”
Denton listed a number of methods AI may be developed responsibly, together with transparency requirements, open sourcing foundational fashions and coverage safeguards.
“AI progress does not have to be catastrophic or dystopian. In fact, these technologies can greatly empower and enhance human productivity and performance across industries. Al does not necessarily have to replace human workers but can rather amplify their capabilities,” Denton mentioned. “The path forward we should strive for is not Al displacing labor but rather augmenting it. We have an opportunity to uplift humanity through optimizing the interplay between human strengths and Al capabilities.”